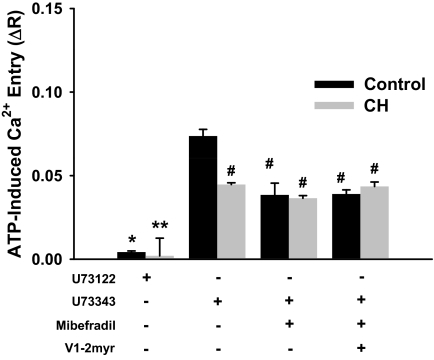
Fig. 5.
Receptor-mediated (ATP) Ca2+ influx operates through a PLC-dependent mechanism that potentially requires PKCε to activate T-type VGCCs in endothelium from controls but not CH pulmonary arteries. PLC-dependent signaling through PKCε, and T-type VGCCs in ATP-induced Ca2+ entry was examined in endothelium from control and CH pulmonary arteries. Experiments were conducted after the SOC entry response in the presence of U73122 (3 μM), U73343 (3 μM), mibefradil (10 μM), and V1-2myr (10 μM). Values are expressed as means ± S.E. (n = 5/group). P ≤ 0.05: *, versus inactive analog control; **, versus inactive analog CH; #, versus U73343 control.