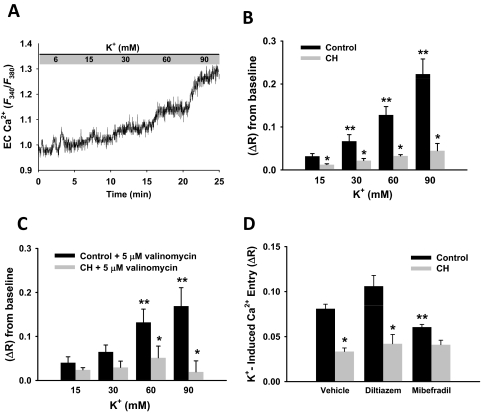
Fig. 6.
Endothelial cell Ca2+ increases in response to increasing K+ concentrations. A, representative trace illustrating endothelial cell Ca2+ response to incremental K+ concentrations measured by Fura-2 in control cells. B, summary data illustrating K+-dependent Ca2+ responses in endothelium from control and CH pulmonary arteries. KCl-induced Ca2+ responses were less at all K+ concentrations in cells from CH rats compared with controls. C, K+-induced Ca2+ influx was also performed in the presence of the K+-selective ionophore valinomycin (5 μM). Values are expressed as means ± S.E. (n = 4/group). P ≤ 0.05: *, versus control; **, versus 15 mM K+ concentration. D, summary data illustrating reduced Ca2+ entry after CH in response to 60 mM K+ and the effects of VGCC channel inhibition in control endothelial cells. Diltiazem (50 μM) and 10 μM mibefradil were used to selectively inhibit L-type and T-type VGCCs, respectively. ΔR is defined by change in F340/F380. Values are expressed as means ± S.E. (n = 4/group). P ≤ 0.05: *, versus control; **, versus control vehicle and control diltiazem.