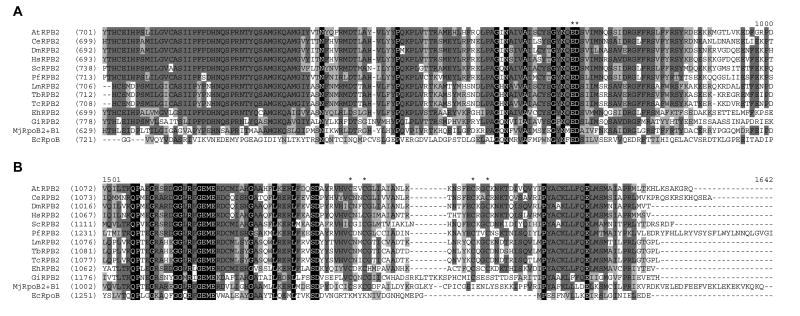
Fig. 1.
Sequence conservation of RPB2 subunits from several species. Protein sequences of RPB2 homologues from Arabidopsis thaliana (At), Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce), Drosophila melanogaster (Dm), Homo sapiens (Hs), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc), Plasmodium falciparum (Pf), Leishmania major (Lm), Trypanosoma brucei (Tb), Trypanosoma cruzi (Tc), Entamoeba histolytica (Eh), Giardia intestinalis (Gi), Methanococcus jannaschii subunits B2 and B1 (MjRpoB2+B1) and Escherichia coli RNA polymerase subunit β (EcRpoB) were aligned using the default setting of AlignX module of VectorNTI (Invitrogen). Multiple sequence alignment of the regions surrounding the active site and C-terminal zinc-binding domain are showing in panels A and B, respectively. Asterisks above the sequence indicate conserved amino acids implicated in these functions. Amino acid residues conserved in all sequences are shaded in black; those conserved in more than 50% of the sequences are shaded in dark grey, while those that which show conservative replacement are shaded in light grey.