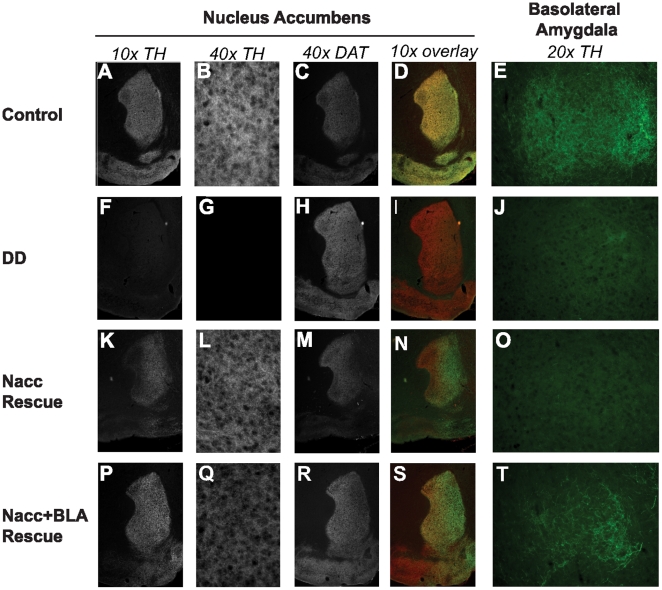
Figure 1. Selective restoration of TH in virally-rescued DD mice.
A–E) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) results for a control mouse. A) Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) stain in the nucleus accumbens (NAc). B) 40x magnification of TH stain. C) Stain for dopamine transporter (DAT) in NAc. D) Merged image of TH and DAT stain showing extensive overlap of the two signals. E) TH stain in basolateral amygdala (BLA) shown at 20x. F–J) IHC results for a non-rescued DD mouse. F) Complete absence of TH in NAc. G) 40x magnification demonstrating lack of TH in NAc. H) DAT stain. I) Merged image of TH and DAT illustrating lack of TH in the NAc. J) TH in BLA (20x) is almost undetectable. K–O) Representative IHC from NAc-rescued DD mouse. K) TH was largely restored in the NAc. L) 40x magnification illustrating rescue of TH. M) DAT staining in NAc-rescued DD mouse. N) Merged image of TH and DAT illustrating large extent of TH restoration in NAc. O) TH in BLA (20x) remains at low, non-injected levels. P–T) Representative IHC from DD mouse injected into the NAc and BLA. P) Robust restoration of TH to the NAc. Q) 40x magnification demonstrating TH rescue. R) DAT staining. S) Merged image of TH and DAT showing extensive restoration of TH to NAc. T) TH is restored to higher levels in NAc and BLA rescued DD mice.