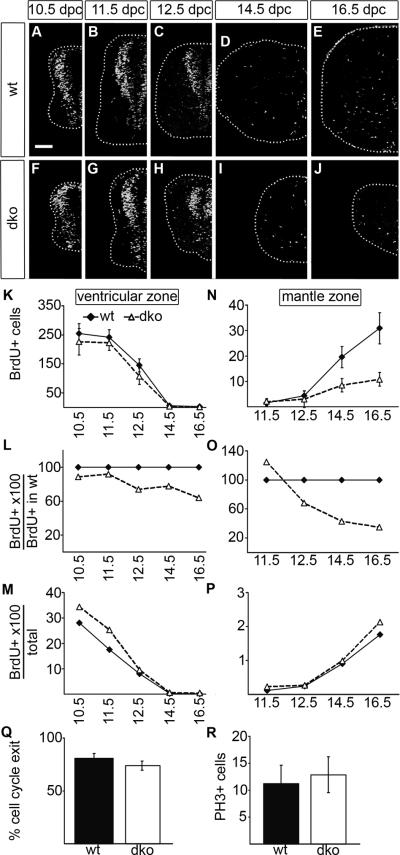
Fig. 5. Proliferation and cell cycle parameters in the embryonic SC of wildtype mice and mice with SoxC deficiencies.
(A–J) BrdU integrated into the cellular DNA within a 1 hour period prior to embryo preparation was detected by anti-BrdU antibodies on transverse thoracic level sections of wildtype (wt) (A–E) and Sox4Δ/Δ Sox11lacZ/lacZ (dko) (F–J) embryos at 10.5 dpc (A,F), 11.5 dpc (B,G), 12.5 dpc (C,H), 14.5 dpc (D,I) and 16.5 dpc (E,J). Only one half of the SC is shown placed on a black background with its circumference indicated by a dotted line. Scale bar in A is valid for all panels and corresponds to 100 μm. (K–P) The numbers of BrdU-labelled cells were separately determined for VZ (K,L,M) and mantle zone (N,O,P) in one half of the SC per section for wildtype (wt, filled diamond) and Sox4Δ/Δ Sox11lacZ/lacZ (dko, open triangle) embryos at various times and are presented as absolute numbers (K,N), relative to wildtype numbers of BrdU-labelled cells in the respective zone (L,O) and relative to overall cell numbers in VZ (M) or mantle zone (P) in the respective genotype. Reductions in cell number relative to the age-matched wildtype were statistically significant (P <0.001) for BrdU-positive cells in the mantle zone of Sox4Δ/Δ Sox11lacZ/lacZ SC at 14.5 and 16.5 dpc as determined by Student's t test. (Q) BrdU integrated into the cellular DNA 24 h prior to embryo preparation was detected by anti-BrdU antibodies on transverse thoracic level sections of wildtype (wt) and Sox4Δ/Δ Sox11lacZ/lacZ (dko) embryos at 14.5 dpc and compared to Ki67-immunohistochemistry. The number of cells that were BrdU-positive but Ki67-negative were determined to quantify cell cycle exit. (R) Mitotic cells were detected with antibodies against phospho-Histone H3 (PH3) in wildtype (wt) and Sox4Δ/Δ Sox11lacZ/lacZ (dko) embryos at 12.5 dpc. Differences between genotypes are not statistically significant in (Q,R).