Abstract
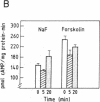
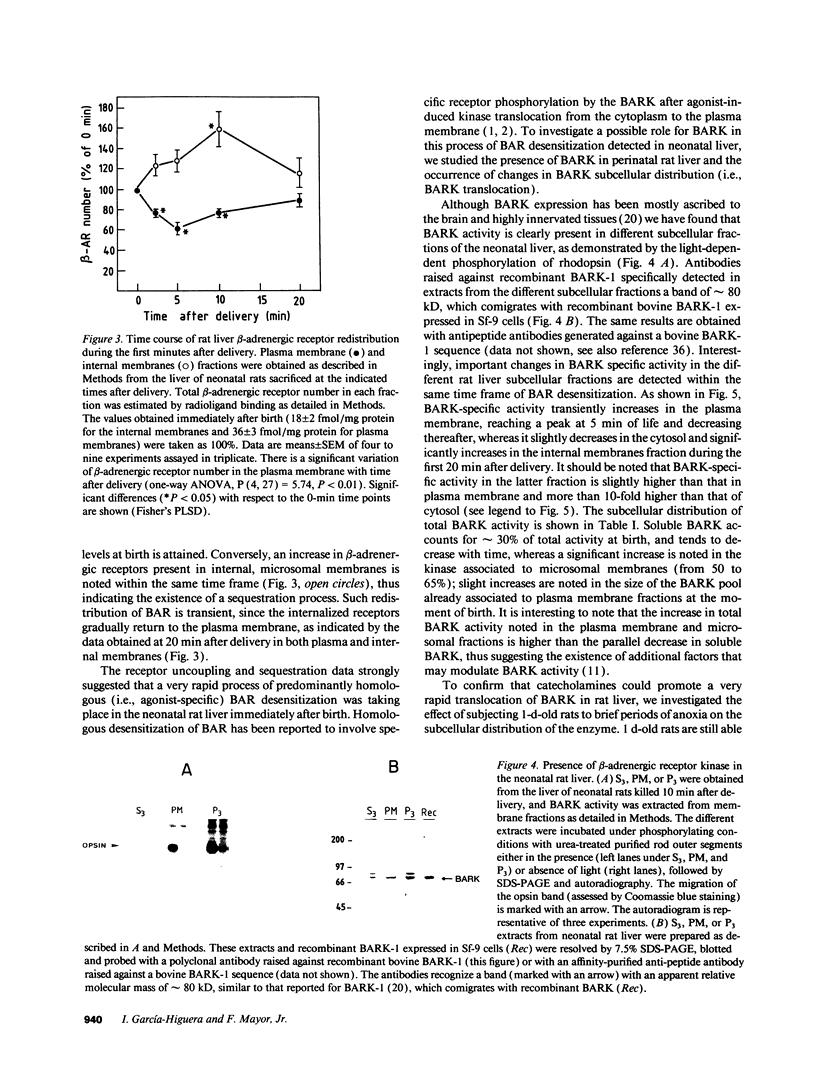
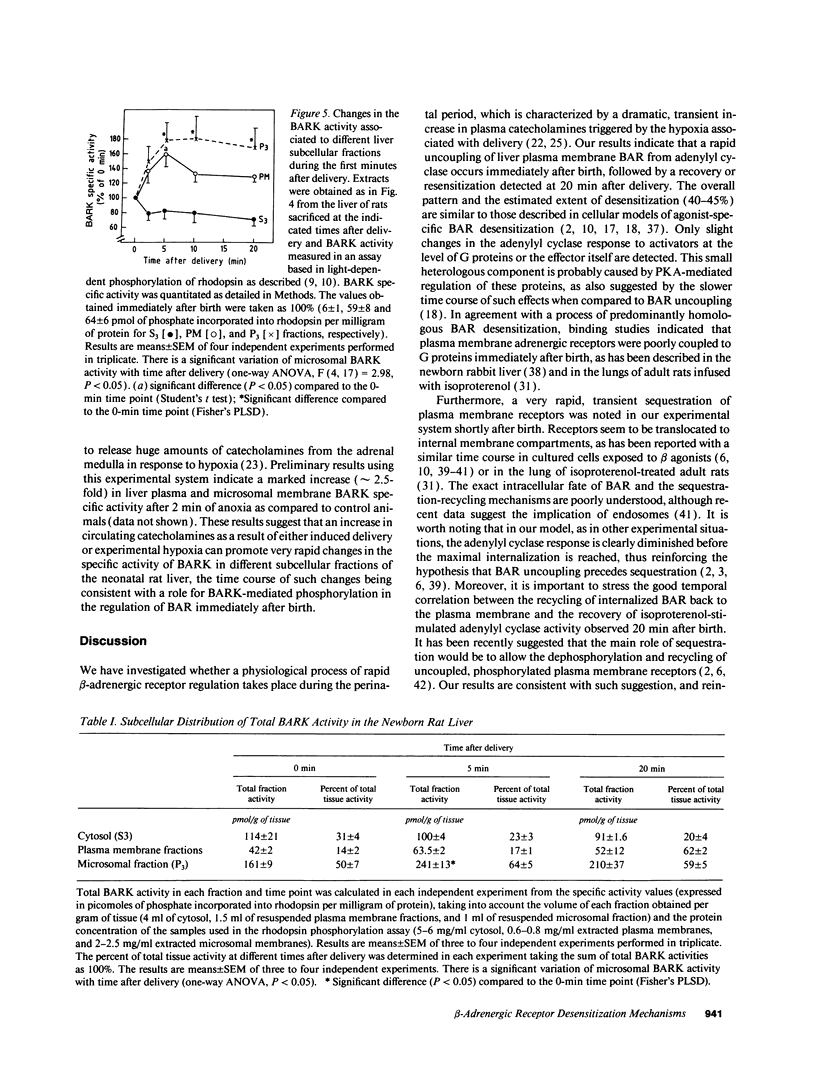
Exposure of beta-adrenergic receptors (BAR) to agonists often leads to a rapid loss of receptor responsiveness. The proposed mechanisms of such rapid receptor desensitization include receptor phosphorylation by either cAMP-dependent protein kinase or the specific beta-adrenergic receptor kinase (BARK), leading to functional uncoupling from adenylyl cyclase and sequestration of the receptors away from the cell surface. To evaluate the physiological role of such mechanisms, we have investigated whether rapid regulation of BAR occurs in the neonatal rat liver immediately after birth, a physiological situation characterized by a dramatic but transient increase in plasma catecholamines. We have detected a rapid, transient uncoupling of liver plasma membrane BARs from adenylyl cyclase (corresponding to a desensitization of approximately 45%) within the first minutes of extrauterine life, followed by a transient sequestration of approximately 40% of the BARs away from the plasma membrane. In agreement with such pattern of desensitization, we have detected (by enzymatic and immunological assays) rapid changes in BARK specific activity in different neonatal rat liver subcellular fractions that take place within the same time frame of BAR uncoupling and sequestration. Our results provide new evidence on the potential role of BAR desensitization mechanisms in vivo and suggest that they are involved in modulating catecholamines actions at the moment of birth. Furthermore, our data indicate that in addition to its suggested role as a rapid modulator of adrenergic receptor function at synapse, rapid BARK-mediated receptor regulation may have functional relevance in other tissues in response to high circulating or local levels of agonists.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer P. H., Müller S., Puzicha M., Pippig S., Obermaier B., Helmreich E. J., Lohse M. J. Phosducin is a protein kinase A-regulated G-protein regulator. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):73–76. doi: 10.1038/358073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Bouvier M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of adenylyl cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptors. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:405–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., DeBlasi A., Stone W. C., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: primary structure delineates a multigene family. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):235–240. doi: 10.1126/science.2552582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Mayor F., Jr, Somers R. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin by beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):869–872. doi: 10.1038/321869a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Mayor F., Jr, Staniszewski C., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Purification and characterization of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9026–9032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonay P., Hughes R. C. Purification and characterization of a novel broad-specificity (alpha 1----2, alpha 1----3 and alpha 1----6) mannosidase from rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 10;197(1):229–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow M. R., Ginsburg R., Minobe W., Cubicciotti R. S., Sageman W. S., Lurie K., Billingham M. E., Harrison D. C., Stinson E. B. Decreased catecholamine sensitivity and beta-adrenergic-receptor density in failing human hearts. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 22;307(4):205–211. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207223070401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang T. T., Sallese M., Ambrosini G., Parruti G., De Blasi A. High expression of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase in human peripheral blood leukocytes. Isoproterenol and platelet activating factor can induce kinase translocation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6886–6892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Kunkel M. W., Friedman J., Goka T. J., Johnson J. A. Activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase is required for heterologous desensitization of adenylyl cyclase in S49 wild-type lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. From ligand binding to gene expression: new insights into the regulation of G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jan;17(1):37–39. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90425-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuezva J. M., Burkett E. S., Kerr D. S., Rodman H. M., Patel M. S. The newborn of diabetic rat. I. Hormonal and metabolic changes in the postnatal period. Pediatr Res. 1982 Aug;16(8):632–637. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198208000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Thorner J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Model systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:653–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Higuera I., Mayor F., Jr Rapid agonist-induced beta-adrenergic receptor kinase translocation in C6 glioma cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 4;302(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80285-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Higuera I., Penela P., Murga C., Egea G., Bonay P., Benovic J. L., Mayor F., Jr Association of the regulatory beta-adrenergic receptor kinase with rat liver microsomal membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1348–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sáinz J. A., Michel B. Homologous beta-adrenergic desensitization in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):331–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2460331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Regulation of receptor expression by agonists: transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Jun;14(6):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90124-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Bouvier M., O'Dowd B. F., Irons G. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation sites on two domains of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor are involved in distinct pathways of receptor desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12657–12665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Turning off the signal: desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2881–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Arinze I. J. Activation of glycogenolysis in neonatal liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):853–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Graham S. M., Whitsel C., Arinze I. J. Hepatic adenylate cyclase. Development-dependent coupling to the beta-adrenergic receptor in the neonate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10826–10832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. Adrenergic receptors as models for G protein-coupled receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1992;15:87–114. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.15.030192.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagercrantz H., Slotkin T. A. The "stress" of being born. Sci Am. 1986 Apr;254(4):100–107. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0486-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasa I., Castón J. R., Fernández-Herrero L. A., de Pedro M. A., Berenguer J. Insertional mutagenesis in the extreme thermophilic eubacteria Thermus thermophilus HB8. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(11):1555–1564. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Andexinger S., Pitcher J., Trukawinski S., Codina J., Faure J. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Receptor-specific desensitization with purified proteins. Kinase dependence and receptor specificity of beta-arrestin and arrestin in the beta 2-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin systems. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8558–8564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Multiple pathways of rapid beta 2-adrenergic receptor desensitization. Delineation with specific inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3202–3211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Codina J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. beta-Arrestin: a protein that regulates beta-adrenergic receptor function. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1547–1550. doi: 10.1126/science.2163110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Benovic J. L. Inhibition of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase prevents rapid homologous desensitization of beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3011–3015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor F., Jr, Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Somatostatin induces translocation of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase and desensitizes somatostatin receptors in S49 lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6468–6471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor F., Jr, Pagés M., Díez-Guerra J., Valdivieso F., Mayor F. Effect of postnatal anoxia on bilirubin levels in rat brain. Pediatr Res. 1985 Feb;19(2):231–236. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198502000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky H. J., Ransnas L. A. Fitting curves to data using nonlinear regression: a practical and nonmathematical review. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):365–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palczewski K., Benovic J. L. G-protein-coupled receptor kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Oct;16(10):387–391. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90157-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher J. A., Inglese J., Higgins J. B., Arriza J. L., Casey P. J., Kim C., Benovic J. L., Kwatra M. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Role of beta gamma subunits of G proteins in targeting the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase to membrane-bound receptors. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1264–1267. doi: 10.1126/science.1325672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth N. S., Campbell P. T., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Lohse M. J. Comparative rates of desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptors by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase and the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6201–6204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler F. J., Slotkin T. A. Adrenomedullary function in the neonatal rat: responses to acute hypoxia. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snavely M. D., Mahan L. C., O'Connor D. T., Insel P. A. Selective down-regulation of adrenergic receptor subtypes in tissues from rats with pheochromocytoma. Endocrinology. 1983 Jul;113(1):354–361. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-1-354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin M., Simons P. Rapid and reversible disappearance of beta-adrenergic cell surface receptors. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):187–190. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01145.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser R. H., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-agonist- and prostaglandin E1-induced translocation of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: evidence that the kinase may act on multiple adenylate cyclase-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6362–6366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser R. H., Stiles G. L., Lefkowitz R. J. Translocation and uncoupling of the beta-adrenergic receptor in rat lung after catecholamine promoted desensitization in vivo. Endocrinology. 1984 Oct;115(4):1392–1400. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-4-1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su Y. F., Harden T. K., Perkins J. P. Catecholamine-specific desensitization of adenylate cyclase. Evidence for a multistep process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7410–7419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub L. M., Sagi-Eisenberg R. Purification of p100, a protein antigenically related to the signal transducing G proteins Gt and Gi. Evidence for an adaptin-like protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24642–24649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vatner D. E., Vatner S. F., Nejima J., Uemura N., Susanni E. E., Hintze T. H., Homcy C. J. Chronic norepinephrine elicits desensitization by uncoupling the beta-receptor. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1741–1748. doi: 10.1172/JCI114357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldo G. L., Northup J. K., Perkins J. P., Harden T. K. Characterization of an altered membrane form of the beta-adrenergic receptor produced during agonist-induced desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13900–13908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. S., Lefkowitz R. J., Hausdorff W. P. Beta-adrenergic receptor sequestration. A potential mechanism of receptor resensitization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaremba T. G., Fishman P. H. Desensitization of catecholamine-stimulated adenylate cyclase and down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors in rat glioma C6 cells. Role of cyclic AMP and protein synthesis. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;26(2):206–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Zastrow M., Kobilka B. K. Ligand-regulated internalization and recycling of human beta 2-adrenergic receptors between the plasma membrane and endosomes containing transferrin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3530–3538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]