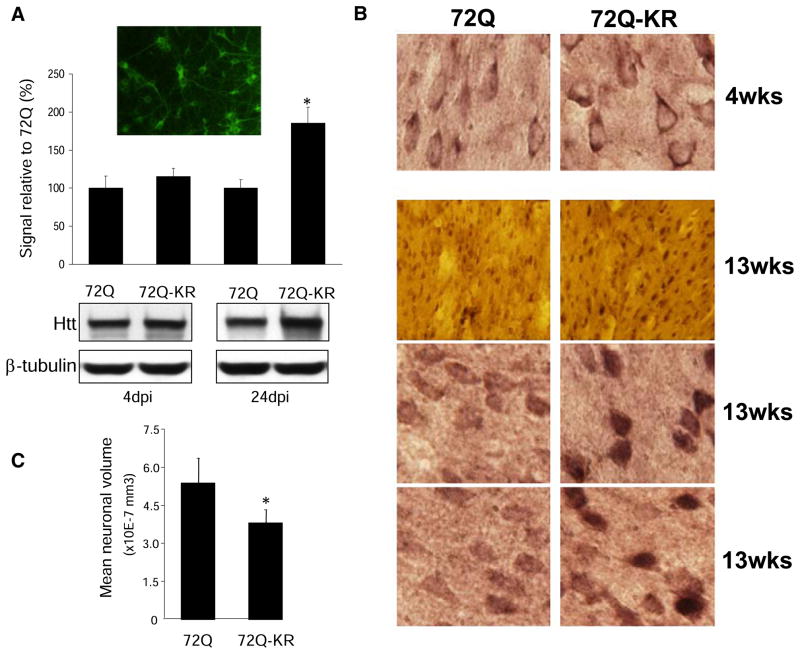
Figure 2. Acetylation-Resistant Mutant Htt Accumulates in Cultured Neurons and in Mouse Brains.
(A) Rat primary cortical neurons were transduced with acetylated (lenti-Htt571-72Q) or acetylation-resistant mutant Htt (lenti-Htt571-72Q-KR) on DIV2. More than 90% of neurons expressed lenti-Htt (Ab1 antibody) (inset). Twenty-four days post-infection lenti-Htt571-72Q-KR significantly accumulated compared to lenti-Htt571-72Q. *p < 0.01 for three independent experiments.
(B) Lentiviral delivery of mutant Htt in mouse cortex and striatum. Expression of lenti-Htt571-72Q and lenti-Htt571-72Q-KR Htt in contralateral brain sections was examined at 4 and 13 weeks after injection by immunostaining with EM48 antibody against mutant Htt. Serial sections from at least ten mice in each group were examined. Representative sections show predominantly cytoplasmic neuronal expression of lenti-Htt571-72Q and cytoplasmic and nuclear expression of lenti-Htt571-72Q-KR. Magnification 40× and 100×.
(C) Neuronal volumes were significantly decreased in lenti-Htt571-72Q-KR compared to lenti-Htt571-72Q injected mice. Unbiased stereological analysis (Micro-BrightField) was performed 13 weeks after injection. Graphs represent means ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of five animals per group; *p < 0.01 compared to 72Q.