Fig. 2.
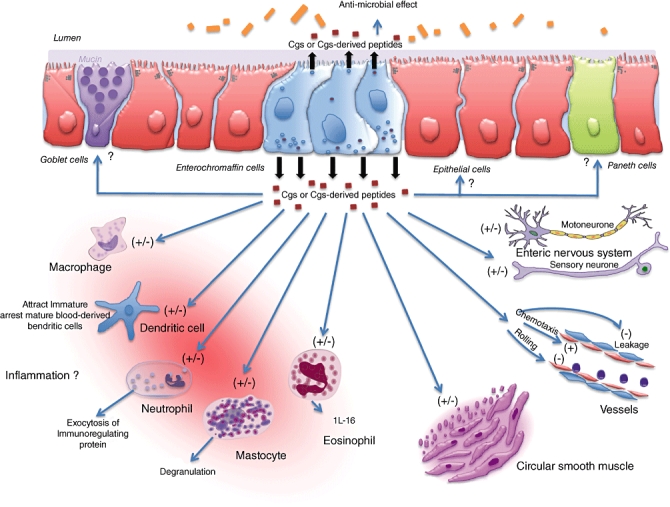
Putative role of chromogranins (Cgs) in immune activation and inflammation. Luminal or internal inflammatory stimuli causes alteration in Cgs or Cgs-derived peptides release. They may act locally on paneth, globet and epithelial cells as well as on immune cells, such as macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophil, mastocytes and eosinophils. Endothelial permeability, chemotaxis, rolling, smooth muscle contractility and the enteric nervous system can also be modulated. IL: interleukin; (−) inhibition; (+) activation.
