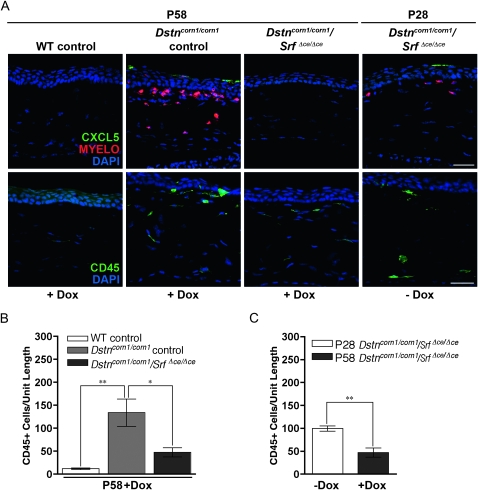
Figure 4.—
CXCL5 expression and inflammatory cell recruitment in WT control, Dstncorn1/corn1 control, and Dstncorn1/corn1/SrfΔce/Δce cornea. (A, top) CXCL5 is detectable in the corneal epithelium and neutrophils of Dox-induced Dstncorn1/corn1 control mice and Dstncorn1/corn1/SrfΔce/Δce cornea prior to Dox induction. CXCL5 is no longer detectable in the corneal epithelium of Dstncorn1/corn1/SrfΔce/Δce mice following Dox induction, demonstrating a reversal of the expression of this neutrophil chemoattractant. (A, bottom) Immunofluorescence for the pan-leukocyte marker CD45 shows a high level of inflammation in Dox-treated Dstncorn1/corn1 control and Dstncorn1/corn1/SrfΔce/Δce cornea prior to Dox treatment. Inflammation decreases in Dox-induced Dstncorn1/corn1/SrfΔce/Δce mice. All slides were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Bar, 20 μm. (B) Quantification of the CD45 positive cells demonstrated significantly fewer inflammatory cells in Dstncorn1/corn1/SrfΔce/Δce cornea as compared to Dstncorn1/corn1 control mice treated with Dox. (C) Quantification of the CD45 positive cells confirmed a significant regression of the inflammatory phenotype following Dox induction in Dstncorn1/corn1/SrfΔce/Δce mice. Error bars, SEM. * denotes statistical significance. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.