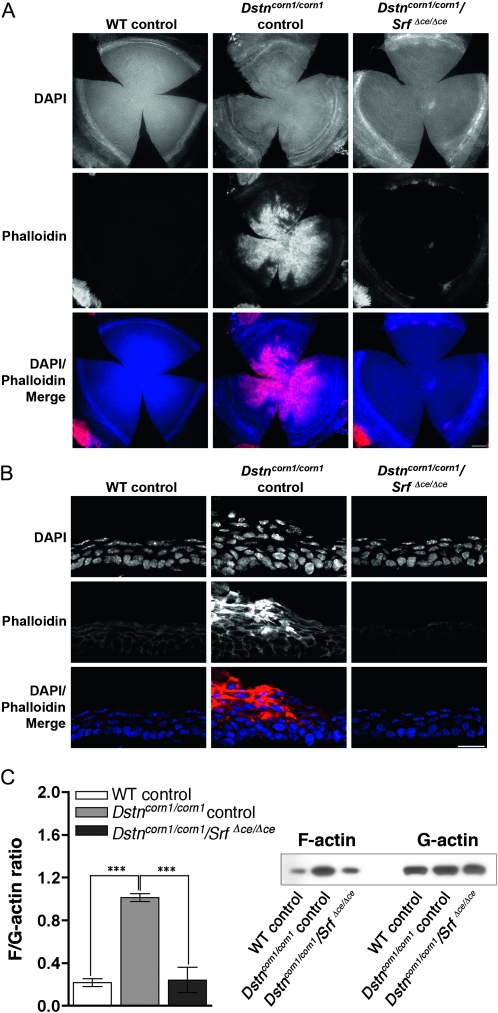
Figure 6.—
F-actin in the corneas of Dox-induced WT control, Dstncorn1/corn1 control, and Dstncorn1/corn1/SrfΔce/Δce cornea. (A) Immunofluorescence for F-actin (phalloidin, red) shows that F-actin accumulation is prevented upon SRF ablation throughout the corneal epithelium in Dstncorn1/corn1/SrfΔce/Δce cornea except in small areas of the most peripheral region. Bar, 200 μm. (B) Cell shape and architecture of Dox-induced Dstncorn1/corn1/SrfΔce/Δce corneal epithelium has been restored to a more normal appearance and F-actin accumulation no longer occurs. Bar, 20 μm. (C, left) Quantification of the overall changes of F-actin and G-actin in the cornea shows that SRF activation leads to significant increases in the F/G-actin ratio. Error bars, SEM. * denotes statistical significance. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (C, right) Immunoblotting showed that SRF activation affects the filamentous, but not globular actin level.