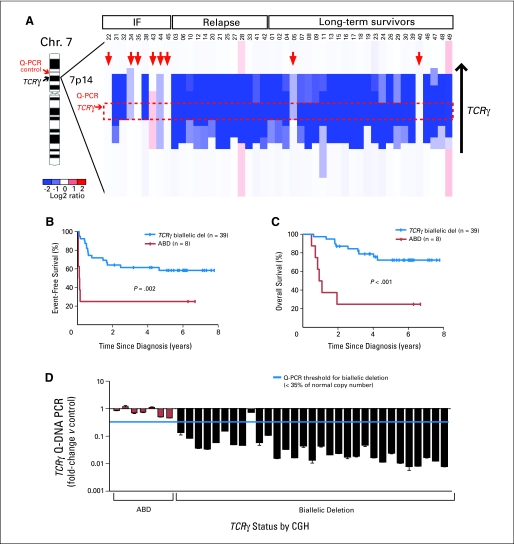
Fig 1.
Relationship of absence of biallelic TCRγ locus deletion (ABD) status to clinical outcome. (A) Array comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) data obtained from diagnostic T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) specimens from 47 children with T-ALL treated on Children's Oncology Group (COG) P9404 or Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) 00-01 protocols are shown as a dChip plot of CGH segmented log2 copy number ratios at the TCRγ locus. Red arrows denote patients with ABD, with the threshold for biallelic TCRγ deletion defined as a CGH log2 ratio of −1.5, corresponding to 35% of normal copy number. The red box denotes the location of the intron between the most 3′ V pseudoexon (TRGV11) and the most 5′ J exon (TRGJP1), which should be involved by any deletion within the TCRγ locus as a result of V-J recombination. Location of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer pairs at TCRγ and at the ANLN control, which were used for the quantitative DNA PCR (Q-PCR) assay to detect ABD, are indicated. (B, C) Kaplan-Meier event-free and overall survival rates for patients with T-ALL classified by ABD status. Tick marks indicate patients still at risk. (D) ABD status by CGH was validated by Q-PCR, with use of the TCRγ and ANLN control primer whose locations are shown in (A). Results of the CGH and DNA PCR analyses were concordant in 97% (37 of 38) samples. IF, induction failure; Chr, chromosome.