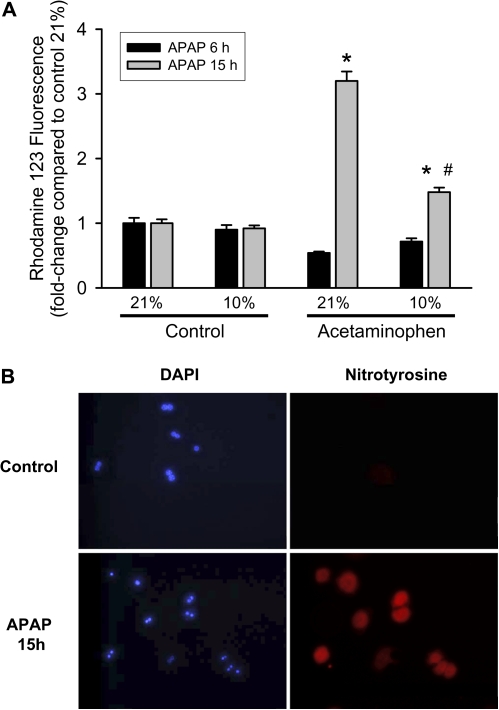
FIG. 7.
Nitrotyrosine staining and rhodamine fluorescence as indicators of reactive nitrogen formation. (A) Rhodamine 123 fluorescence (reflecting RNS) in mitochondria after treatment with 5mM APAP for 6 or 15 h at 21 or 10% oxygen. Primary mouse hepatocytes were isolated and treated with APAP; cells were loaded with dihydrorhodamine after 6 or 15 h, lysed, and fluorescence measured on a spectrofluorometer. Data are expressed as mean ± SE of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 (compared with respective control) and #p < 0.05 (compared with 21% oxygen). (B) Cells were isolated as described in the Materials and Methods section and cultured on glass coverslips at 21% oxygen for 15 h. Cells were then fixed and stained for nitrotyrosine protein adducts as indicator for peroxynitrite formation. Panels on the left show staining of nuclei with DAPI, and on the right panels, nitrotyrosine protein adducts are visualized.