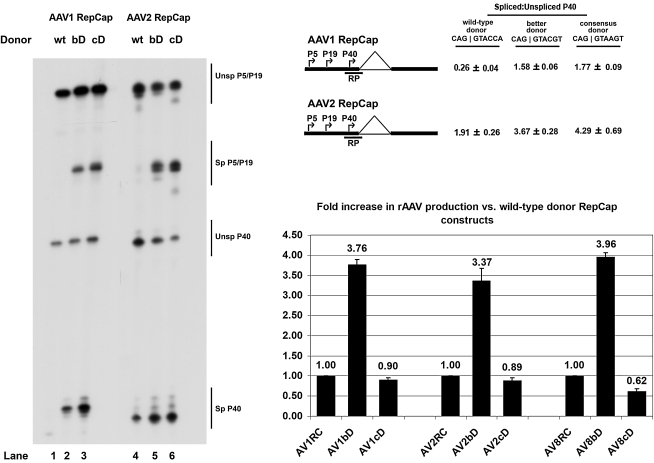
FIG. 1.
Improvement of the nonconsensus AAV donor significantly enhanced overall pre-mRNA splicing, capsid production, and rAAV production. Left: Representative RNase protection assay of AAV1 and AAV2 RepCap plasmids (AV1RC and AV2RC, respectively) with wild-type, “better” (bD), or consensus donor (cD) mutations in the presence of pHelper. Unsp, Unspliced; Sp, Spliced. Top right: Quantification of the relative spliced-to-unspliced ratios of capsid-encoding pre-mRNA. Data are from at least three experiments and show standard deviations. The position of the “RP” RNase protection probe is indicated. Bottom right: Relative levels of rAAV production observed for AAV1, AAV2, and AAV8 with the “better” and consensus donor mutants in relation to levels obtained with the wild-type donors (set to a value of 1.00). Average titers of DNase-resistant rAAV virions per 100-mm dish (with standard deviations in parentheses) were as follows: AV1RC, 1.25 × 1010 (±4.87 × 109); AV1bD, 4.78 × 1010 (±2.16 × 1010); AV1cD, 1.08 × 1010 (±2.75 × 109); AV2RC, 3.43 × 1010 (±1.33 × 1010); AV2bD, 1.15 × 1011 (±4.10 × 1010); AV2cD, 3.04 × 1010 (±1.34 × 1010); AV8RC, 6.97 × 1010 (±2.01 × 1010); AV8bD, 2.78 × 1011 (±9.07 × 1010); AV8cD, 4.45 × 1010 (±1.72 × 1010).