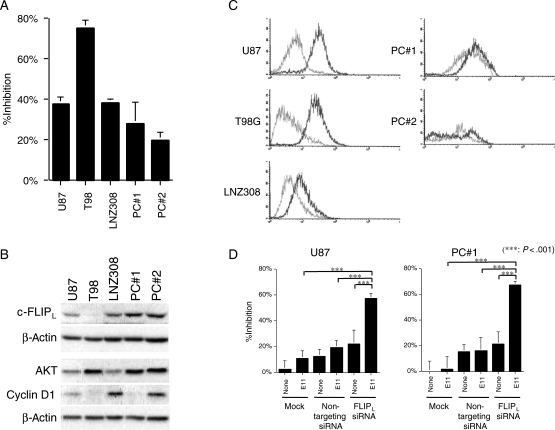
Fig. 8.
Association of relative resistance of primary cultures of glioma cells to anti-DR5 mAbs with altered expression of DR5 and c-FLIPL. (A) Primary glioma cells were less sensitive to anti-DR5 mAb than sensitive glioma cell lines. Cells were treated with E11 (0.1 µg/mL) for 48 hours and then were subjected to the MTT assay. The experiment was repeated 3 times with similar results. (B) Western blot analyses showing expression levels of c-FLIPL, Akt, and cyclin D1 in human glioma cell lines and primary glioma cells. Whole cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting and serially probed with the specific antibodies indicated. High expression of c-FLIPL is observed in primary glioma cells. (C) DR5 cell-surface expression determined by flow cytometry analysis as described in Fig. 4. Primary culture glioma cells tended to have lower cell-surface expression of DR5 than the established GBM cell lines with high sensitivity to E11. (D) siRNA-mediated targeting of c-FLIPL enhances the sensitivity of primary glioma cells to anti-DR5 mAb. Cells were treated as described in Fig. 5 (E11 at 0.01 µg/mL) and then were subjected to the MTT assay. ***P < .001 (Student's t-test). The experiment was repeated 2 times with similar results.