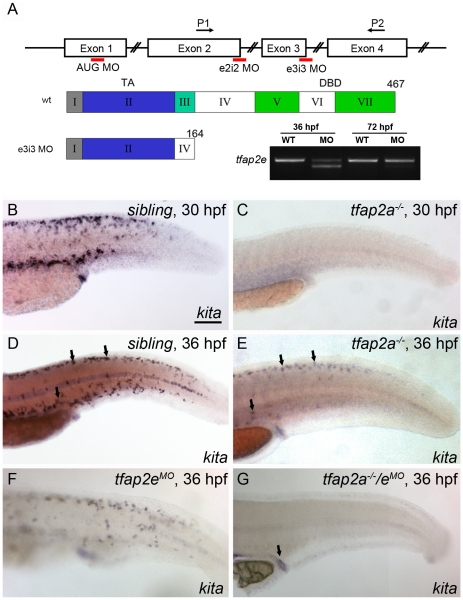
Figure 2. Expression of kita in melanophores is dependent on Tfap2a and Tfap2e.
(A) Top, schematic of the tfap2e gene, showing the target sites of the MOs used in this study; middle, schematic indicating the effects of the tfap2e e3i3 MO on the tfap2e transcript (Roman numerals refer to exons, other numbers refer to amino acids). TA, transactivation domain. DBD, DNA binding domain. The e2i2 MO overlaps the exon 2 splice donor site, the e3i3 MO overlaps the exon 3 splice donor site, and the AUG MO overlaps the translation start site, as indicated in red. P1 and P2 are the primers used for RT-PCR. tfap2e e3i3 causes precise deletion of exon 3, leading to a frame shift and premature stop codon near the beginning of exon 4. Bottom right, Ethidium bromide-stained gel of PCR products generated from cDNA harvested from tfap2e e3i3 MO injected embryos at the indicted stages. The MO has largely lost efficacy by 72 hpf. (B–G) Lateral views of embryos processed to reveal kita expression. (B,C) At 30 hpf, kita expression is readily detected in the dorsum of B) a sibling embryo but not C) a tfap2a mutant. (D, E) At 36 hpf kita expression is detectable in discrete cells in the dorsum of D) sibling embryos (arrows), E) tfap2a mutants (arrows), and F) sibling embryos injected with tfap2e MO, but is undetectable in G), the dorsum of tfap2a mutants injected with a tfap2e MO; kita expression is still detected in the cloaca of this last group (arrow). MOs are co-injected with p53 MO in this and subsequent figures, to prevent cell death in the nervous system (see text). B) Scale bars: 100 µM (applies to B–G).