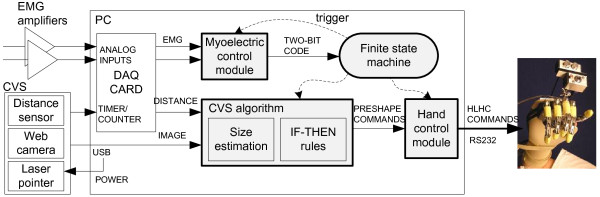
Figure 2.
The implementation of the control system architecture. The hardware comprises: 1) the cognitive vision system (CVS), 2) a two-channel EMG system, and 3) a PC with a data acquisition card. The PC runs a control application implementing a finite state machine that triggers the following modules (gray boxes): the myoelectric control module, the CVS algorithm and the hand control module. The myoelectric module acquires and processes the EMG, generating a two-bit code signalling the activity of the flexor and extensor muscles. This code is the input for the state machine. The CVS algorithm estimates the size of the target object and uses a set of simple IF-THEN rules to select the grasp type and aperture size appropriate to grasp the object. The hand control module implements the selected grasp parameters by sending the commands to the embedded hand controller (HLHC) via an RS232 link.