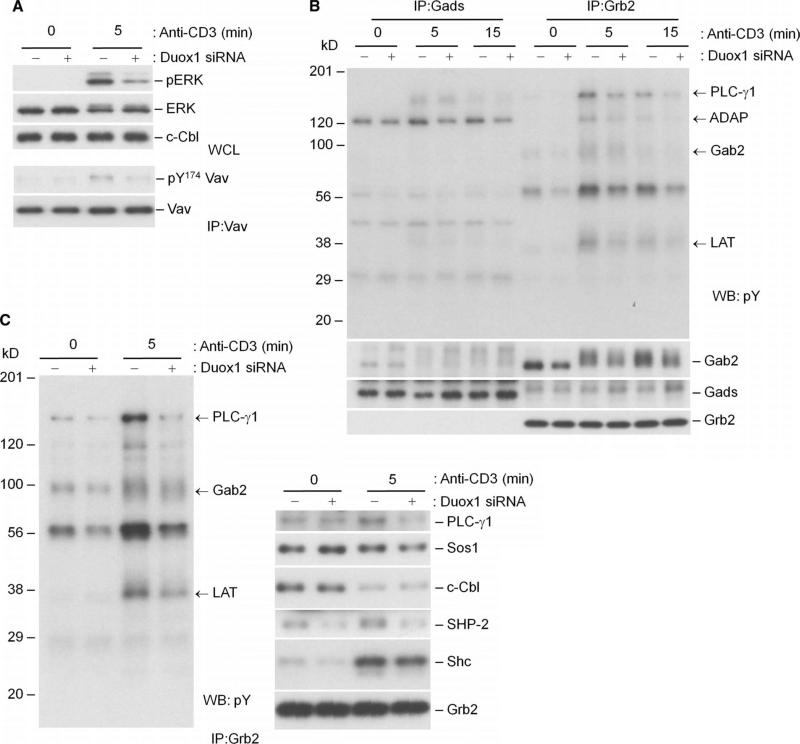
Fig. 7.
Effects of knockdown of Duox1 on TCR-stimulated activation of ERK and signaling phosphoproteins associated with the adaptor proteins Gads and Grb2. CD4+ human T cell blasts were transfected with NT or Duox1-specific siRNAs as described for Fig. 6. (A) TCR-induced phosphorylation of ERK1 and ERK2 was analyzed after 5 min of stimulation by Western blotting of whole-cell lysates with phosphospecific antibodies. Vav1 was immunoprecipitated from the respective cell lysates and analyzed by Western blotting with a phosphospecific (Y174) antibody. Blots were then stripped and analyzed for total Vav1, Lck, and c-Cbl content to control for loading. (B) Gab2 is primarily associated with Grb2 in human T cells, and tyrosine phosphorylation of Grb2-associated proteins is decreased by knockdown of Duox1. CD4+ human T cell blasts were transfected with NT or Duox1-specific siRNAs and stimulated by TCR cross-linking as described for Fig. 6. Gads and Grb2 were serially immunoprecipitated from precleared lysates, and protein phosphorylation was detected by Western blotting analysis with an antibody against phosphotyrosine. The blot was then stripped and analyzed with antibodies against Gab2, Gads, and Grb2. (C) Tyrosine phosphorylation of Grb2-associated proteins is decreased by knockdown of Duox1. Samples immunoprecipitated with antibody against Grb2 were analyzed by Western blotting with an antibody against phosphotyrosine and with other antibodies specific for the coimmunoprecipitated proteins.