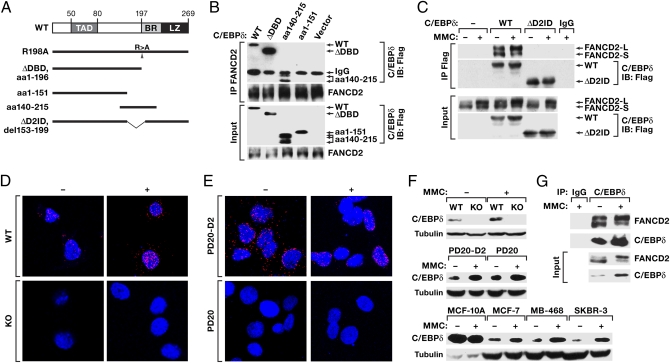
Fig. 1.
Interaction of C/EBPδ and FANCD2 proteins. (A) Schematic representation of mutations in C/EBPδ constructs. R198A is the full-length protein with an R-to-A mutation at residue 198; ΔDBD is a deletion of the DNA-binding basic region (BR) and leucine zipper (LZ); ΔD2ID is a deletion of amino acids 153–199. TAD, transactivation domain. (B) FANCD2 co-IP analysis of 293T cells transfected with Flag-tagged C/EBPδ constructs. Immunoprecipitates (IP) and input samples were analyzed with anti-FANCD2 and anti-Flag antibodies. The multiple bands generated by amino acids 140–215 probably are caused by phosphorylation events because this region harbors several kinase recognition motifs. (C) C/EBPδ co-IP analysis from 293T cells as in B. (D) WT and KO MEFs were treated for 3 h with 5 μg/mL MMC. Fixed cells were incubated with antibodies against C/EBPδ and FANCD2 followed by OLink in situ PLA and fluorescence microscopy using appropriate filters (DAPI, blue; PLA, red). (Fig. S1 shows single-channel images.) (E) FANCD2-deficient cells (PD20) and cells reconstituted with FANCD2 (PD20-D2) were treated for 20 h with 500 ng/mL MMC before processing as described in D. (F) Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates from WT and C/EBPδ-KO MEFs, PD20-D2 or PD20 cells, or the human breast epithelial cell lines MCF-10A, MCF-7, MDA-MB-468, and SKBR-3; treated for 20 h with 1 μg/mL MMC (100 ng/mL for PD20/-D2 cells). (G) Immunoprecipitation from MDA-MB-468 cells with anti-C/EBPδ antibody (Rockland) and input samples were analyzed with anti-FANCD2 and anti-C/EBPδ (BD Biosciences) antibodies.