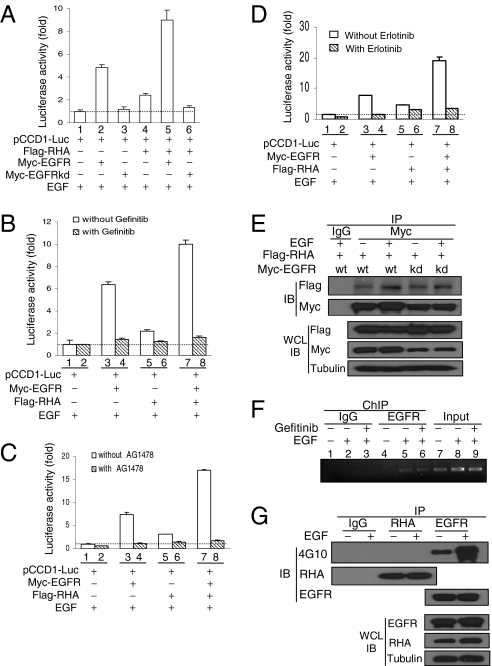
Fig. 3.
Requirement of EGFR tyrosine kinase for EGFR/RHA-induced promoter activity. (A) Abrogation of EGFR/RHA-induced cyclin D1 promoter activity by EGFRkd mutant. (B) Abrogation of EGFR/RHA-induced promoter activity by Gefitinib (10 μM) treatment. (C) Abrogation of EGFR/RHA-induced promoter activity by AG1478 (10 μM) treatment. (D) Abrogation of EGFR/RHA-induced promoter activity by Erlotinib (2.5 μM) treatment. (E) EGFR tyrosine kinase-independent interaction between EGFR and RHA. A total cell lysate from HEK293T cells cotransfected with indicated plasmids was immunoprecipitated with an anti-Myc antibody followed by blotting with an anti-Flag antibody. IB, immunoblotting; IP, immunoprecipitation; WCL, whole-cell lysate. (F) Effects of Gefitinib treatment on the binding of EGFR to cyclin D1 promoter. A431 cells treated with EGF without or with Gefitinib were crosslinked, fractionated, and submitted to ChIP-PCR analysis. (G) There was no detectable tyrosine phosphorylation of endogenous RHA upon EGF stimulation. A431 cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with an anti-EGFR or anti-RHA antibody followed by detection with a tyrosine phosphorylation antibody 4G10.