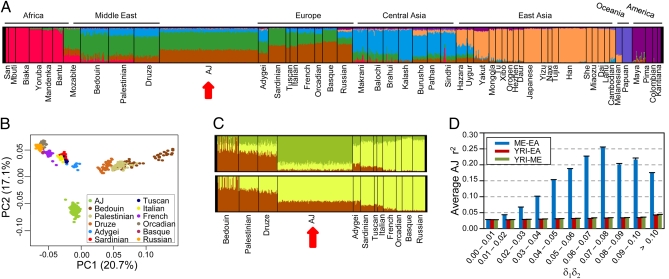
Fig. 2.
Admixture and its relationship with LD. (A–C) Ancestral population clustering and PCA were performed using the combined AJ and HGDP populations. The AJ population was divided into three random subgroups of 157 individuals to better match the population size of the Middle Eastern and European populations in the HGDP dataset. The data shown represent one subgroup, and all three had similar results. (A) Population clustering analysis of AJ and all HGDP individuals for seven, K = 7, theoretical ancestral populations. Each color represents a different ancestral population and each vertical line represents a single individual. The proportion of each color within an individual signifies the fraction of ancestry derived from the color's ancestral population. The red arrow highlights the AJ population. (B) PCA performed using only the AJ, Middle Eastern, and European HGDP populations. (C) Population clustering analysis with K = 3 (Upper) or K = 2 (Lower) ancestral populations, performed using only the AJ, Middle Eastern, and European HGDP populations. (D) The correlation between admixture and LD was determined by plotting the average r2 for all SNP pairs within the given intervals of δ1δ2, where δ1 is the allele frequency difference between the founding populations at locus 1, and δ2 is the frequency difference at locus 2. The legend indicates the populations representing the founding populations: Middle Eastern (ME), European American (EA), or Yoruba in Ibadan, Nigeria (YRI). Error bars show SEM.