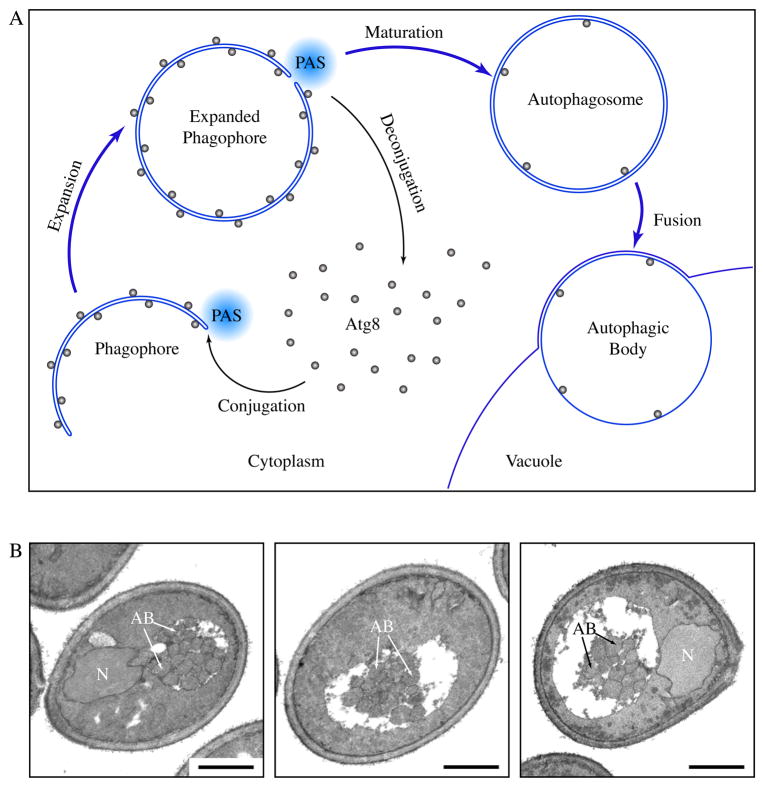
Figure 1.
Formation of autophagosomes and autophagic bodies. (A) Scheme of autophagy in yeast. Autophagosomes are formed through the expansion and deformation of the phagophore at the PAS. During this process, Atg8 is conjugated and recruited to the PAS. It resides on both sides of the phagophore and controls its expansion. At the end of phagophore expansion, most Atg8 molecules are released back to the cytosol through deconjugation. The fully expanded phagophore then matures into an autophagosome. When autophagosomes fuse with the yeast vacuole, the inner vesicles are released into the vacuole lumen, and are now termed autophagic bodies. In pep4Δ cells, autophagic bodies are not degraded. (B) Representative sections of starving pep4Δ yeast cells. atg8Δ pep4Δ cells expressing GFP-Atg8 and grown to mid-log phase were incubated in nitrogen starvation medium for 4 hours and processed for electron microscopy. Autophagic bodies (AB) accumulated as a cluster of single-membrane vesicles in the yeast vacuole. N, nucleus, Scale bar, 1 μm.