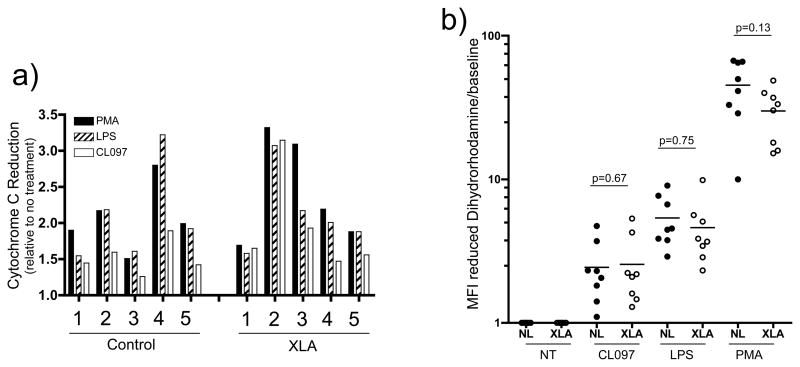
Figure 4. Figure 4a and 4b: TLR induction of respiratory burst.
Isolated neutrophils from normal controls (n=5) or XLA subjects (n=5) were first incubated with cytochrome C, in the presence or absence of SOD, and treated for 20 minutes with CL097 (2.5μg/mL), LPS (100ng/mL) or PMA (10ng/mL). (a) Reduction of cytochrome C by the superoxide radicals produced by neutrophils was assessed at 550nM absorbance. (b) Isolated neutrophils from normal controls (solid circles, n=8) and XLA subjects (open circles, n=8) were incubated with dihydrorhodamine and treated as in Figure 4a, and reduction of dihydrorhodamine to rhodamine was assessed by FACS. These results are represented graphically as MFI of the rhodamine signal. p-values shown are from a two-tailed t-test comparing control and XLA responses within each treatment group.