Fig. 1.
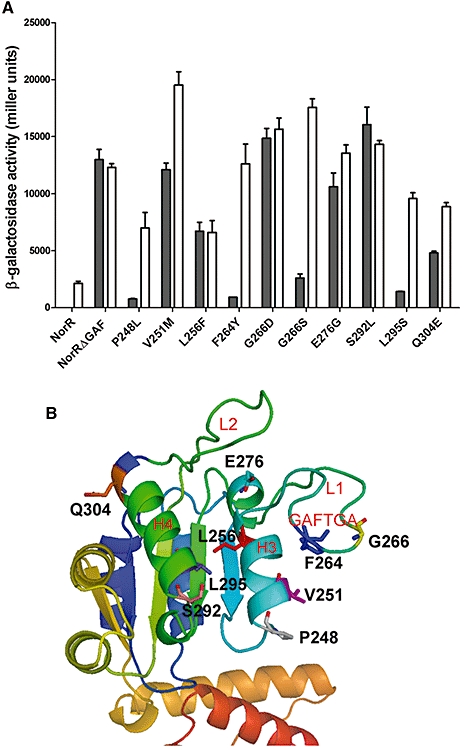
A. Transcriptional activation by NorR AAA+ domain variants in vivo as measured by the norV–lacZ reporter assay. Substitutions are indicated on the x-axis. ‘NorR’ refers to the wild-type protein and ‘NorRΔGAF’ refers to the truncated form lacking the GAF domain (residues 1–170). Cultures were grown either in the absence (black bars) or presence (white bars) of 4 mM potassium nitrite, which induces endogenous NO production. Error bars show the standard error of the three replicates carried out for each condition. B. Structural model of the AAA+ domain of NorR based on the NtrC1 structure (Lee et al., 2003) (1NY5 chain A). The helices and loops (H3 and H4, L1 and L2) involved in nucleotide-dependent conformational changes in bEBPs are labelled in red. Residues that were substituted as a consequence of the PCR mutagenesis of the AAA+ domain are indicated. The F264 and G266 residues form part of the GAFTGA motif that contacts σ54.
