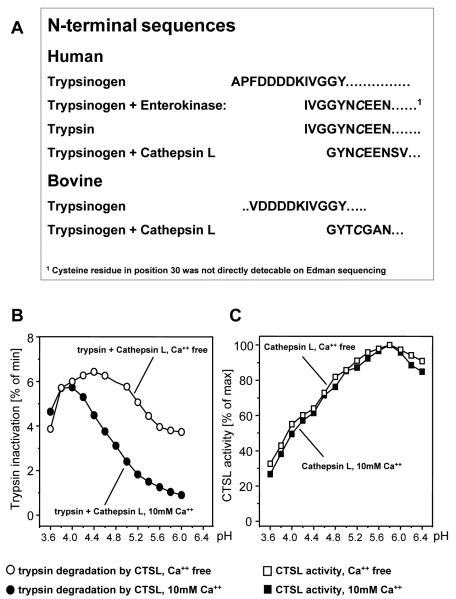
Figure 6. Trypsin cleavage by CTSL and effect of pH and Ca++.
Human cationic trypsinogen or active trypsin were incubated for 3h with CTSL or enterokinase (EK) and submitted to SDS-PAGE followed by N-terminal sequencing. Note that the inactive CTSL-generated protein is three amino acids shorter (IVG) than active trypsin generated by enterokinase (A). Inactivation of human trypsin was measured as residual trypsin activity after incubation with CTSL at the pH indicated (B). Proteolytic cleavage of trypsin by CTSL exhibited a completely different dependence on pH and Ca++ compared to CTSL-cleavage of the peptide substrate (C).