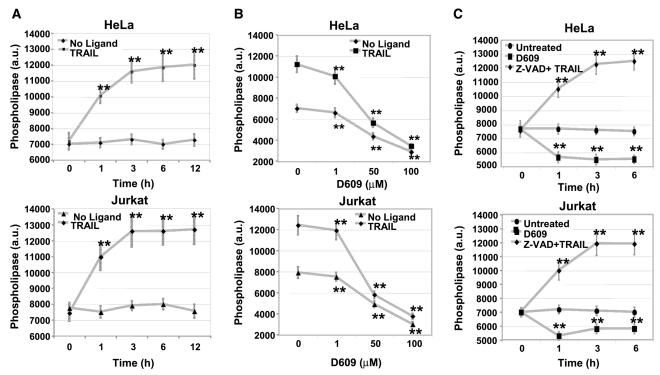
Figure 4.
Phospholipase activity increases in response to TRAIL. A, TRAIL induces activation of phospholipases: HeLa and Jurkat cells were exposed to TRAIL (10 ng/mL) for the indicated times and phospholipase activities were measured using Amplex Red fluorescence (a.u.). Points, mean of three independent experiments; bars, SD. **, 0.05 < P < 0.10, statistically significant two-sided Wilcoxon test comparing 0 hour with 1, 3, 6, and 12 hours. B, TRAIL-induced phospholipase activity is inhibited by D609: HeLa and Jurkat cells were preincubated with D609 at various concentrations for 30 minutes followed by TRAIL treatment as in (A). Points, mean of three independent experiments each done in duplicate; bars, SD. **, 0.05 < P < 0.10, statistically significant two-sided Wilcoxon test compared with control cells (no D609 treatment). C, TRAIL-induced phospholipase activity (A) is not inhibited by z-VAD: HeLa and Jurkat cells were preincubated with 100 μmol/L pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD for 30 minutes followed by TRAIL (10 ng/mL) treatment for 1, 3, and 6 hours. Phospholipase activity was measured as for TRAIL in (A).