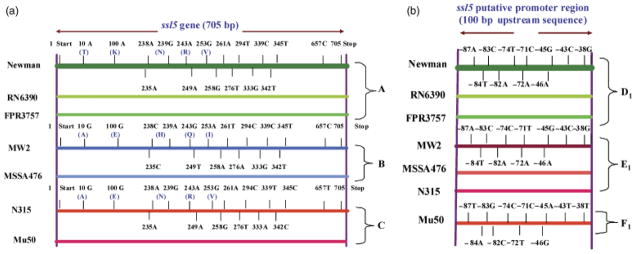
Fig. 2.
(a) Schematic comparison of the ssl5 gene sequences found in seven Staphylococcus aureus strains mentioned in Fig. 1. Different-colored horizontal lines represent different haplotypes (A, B, and C) as indicated on the right side. Only differences in the SNPs and the corresponding amino acid (in parentheses) with respect to the Newman strain are shown. The thick green horizontal line at the top represents the ssl5 sequence from the Newman strain. Short vertical lines above and below the horizontal lines indicate the relative positions of SNPs on the gene. The purple long vertical lines at two ends indicate the 5′ and 3′ ends of ssl5. T, threonine; K, lysine; N, asparagine; R, arginine; V, valine; A, alanine; E, glutamic acid; H, histidine; Q, glutamine; and I, isoleucine. (b) The SNPs in the 100 bp upstream sequences of the ssl5 putative promoter region from the strains mentioned in Fig. 1. The SNPs among seven strains are shown with reference to the Newman strain. The thick green horizontal line at the top represents the ssl5 putative promoter sequence from the Newman strain. Short vertical lines above and below the horizontal lines indicate the relative positions of SNPs. The right vertical line indicates the beginning of the upstream sequence. Three allelic subtypes (D1, E1, and F1) are indicated on the right side and strain names on the left side.