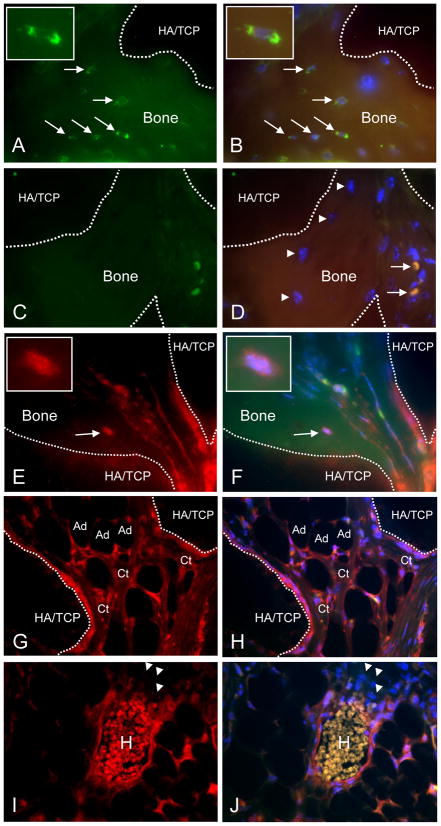
Fig. 4. Immunohistochemical evaluation of CD133dMSC-seeded constructs.
A, B) Human-specific β2M staining (green, FITC channel) of osteocytes within bone formed from CD133BMSCs (arrows) (100X magnification). Dotted lines delineate bone (autofluorescent) and HA/TCP (dark areas). FITC/TRITC merge with DAPI (B). Insets: magnified view of an osteocyte. C, D) Isotype control staining (1 μg/ml IgG, 100X magnification). FITC/TRITC merge with DAPI (D). Arrowheads: osteocytes negative for staining by isotype. Arrows: strongly autofluorescent red blood cells. E, F) Staining for DsRed demonstrates characteristic punctate pattern of mitochondria within a bone-residing osteocyte (TRITC channel, E) and merge (F). Insets: DsRed-positive osteocyte. G, H) DsRed-positive inter-sinusoidal reticular cells, connective tissue (Ct), and adipocytes (Ad) in the implant. I, J) DsRed-positive peri-vascular reticular cells surrounding a sinus. H, Autofluorescent host-derived red blood cells. Arrowheads: Host-derived erythroblasts did not stain positive for DsRed. TRITC channel (E–I). TRITC/FITC merge with DAPI (F–J).