FIG. 4.
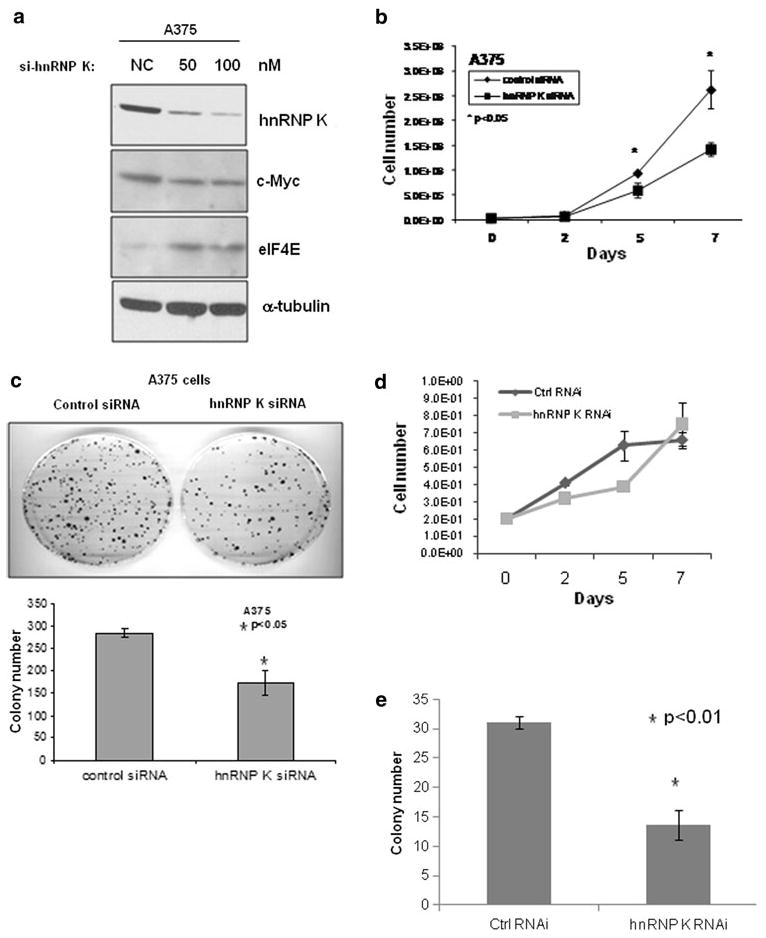
siRNA knock down of hnRNP K inhibited melanoma cell growth and colony formation. a A375 melanoma cells were transfected with negative control (NC) or 50 nM or 100 nM of hnRNP K siRNAs. Cells were harvested and lysed 48 h after transfection, followed by Western blot analysis using hnRNP K, c-myc, eIF4E, and α-tubulin antibodies. b A375 cells were transfected with 50 nM of negative control or hnRNP K siRNA. Then, 24 h after transfection, 2 × 104 cells were seeded into 100-mm plates in triplicate, and cell growth was monitored by counting total cell numbers every 2 or 3 days; or c 1000 cells were seeded into 100-mm plates in triplicate and incubated for 2 weeks to allow colony formation. Then media were removed, and colonies were stained with methylene blue solution. The plates were rinsed with water, and the colony number was counted. d, e Same experiments as described in b and c were repeated in primary human fibroblasts
