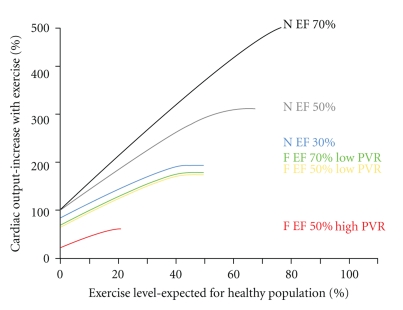
Figure 2.
Relationship of output during exercise, pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), and ventricular function. Cardiac output can increase 5-fold in a normal (N) subject with a biventricular circuit. If ventricular function is impaired, this will first result in decreased maximal output and subsequently in reduced output at low level of exercise. In Fontan patients (F) output is more influenced by PVR than by ventricular function but all have significantly impaired exercise capacity. EF: ejection fraction.