Figure 1.
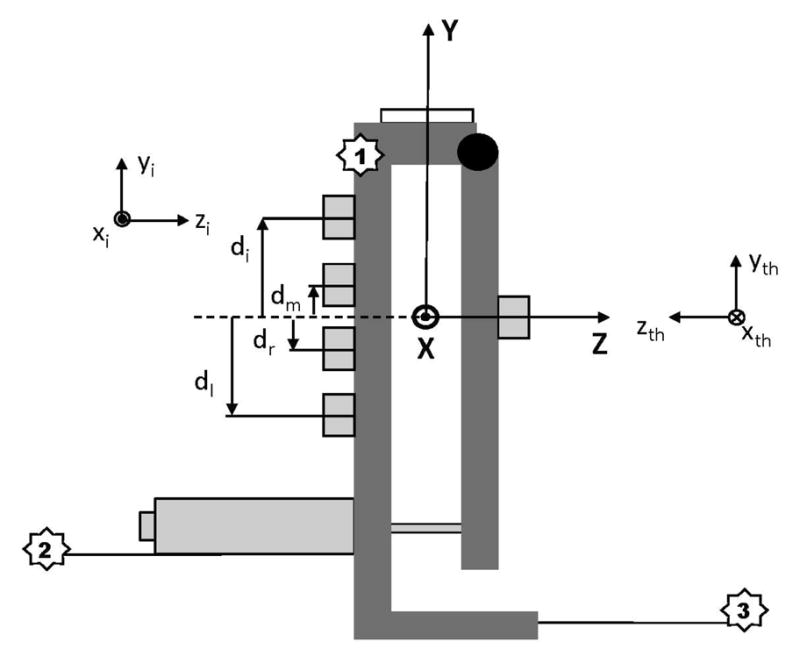
A schematic of the collapsible object. The Nano-17 and Nano-25 sensors (shown as light grey blocks) were attached to vertical aluminum and high density polyethylene bars. A circular bulls-eye (white block) was placed at the geometric center of the object. The global reference frame (X,Y,Z) of the handle is shown as well as the local axes of the thumb and index sensors (xth,yth,zth and xi,yi,zi; respectively). The solenoid that controlled object fragility can be found at the bottom virtual finger-side of the object; the body of the solenoid remained on the virtual finger side of the object at all times. A small metal plunger that moved if the object was collapsed was in contact with the thumb-side of the object. The hinge joint that allowed for object collapse is shown as the black circle on the thumb side of the object. Marker (3 passive markers) locations are denoted by numbered white stars.
