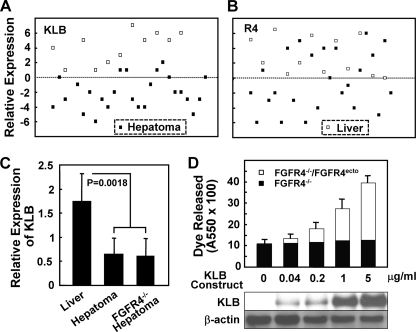
FIGURE 1.
Reduced KLB expression in hepatomas and FGFR4-dependent effect of KLB expression in hepatoma cells. A and B, KLB and FGFR4 expression in human liver and hepatomas. Data from Affymetrix mRNA expression analyses of KLB and FGFR4 in human liver and clinically annotated hepatomas was extracted from the SIB-CleanEx Database and plotted numerically. Closed squares, human hepatoma samples; open squares, normal liver samples. C, reduced KLB expression in mouse hepatomas. The samples were taken from DEN-initiated hepatomas from normal and FGFR4-deficient (FGFR4−/−) mice as described (29). The relative expression of KLB mRNA was determined by quantitative PCR. The indicated data are the means ± S.D. from triplicate analyses of 10 normal liver and 12 hepatoma samples. D, FGFR4-dependent increase in cell death induced by expression of KLB in mouse hepatoma cells. KLB was transiently expressed by the addition of the indicated amounts of the KLB-pEF1a construct to hepatoma cells from FGFR4-deficient mice (FGFR4−/−) or cells (FGFR4−/−/FGFR4ecto) in which FGFR4 had been restored by stable transfection (29). Cell death was assessed by the uptake and release of APOPercentageTM dye. The indicated data are the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments with replicate analyses. FGFR4 expression levels (29) and the indicated KLB expression levels were assessed by immunoblotting of whole cell lysates using β-actin as the loading control.