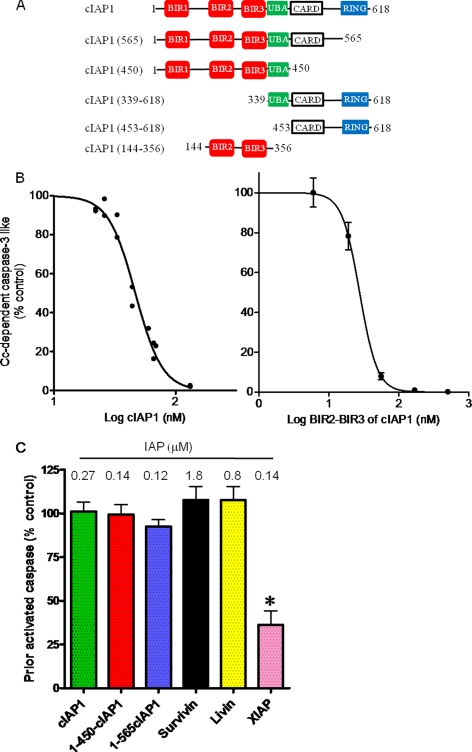
FIGURE 1.
cIAP1 potently blocks cytochrome c-dependent apoptosome activation of procaspase-3-like activity but does not affect already activated caspase-3-like activity. A, schematic of wild-type cIAP1 and truncation mutants. BIR domains and CARD motifs mediate protein-protein interactions. The UBA motif enables binding of Lys-63-linked polyubiquitin chains. RING binds ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. B, inhibition of the cytochrome c-dependent apoptosome by cIAP1 and the BIR2-BIR3 segment of cIAP1. Cytochrome c (Cc)-dependent apoptosome activation of caspase-3 was assayed using an S100 preparation and the indicated concentrations of GST-cIAP1 and the BIR2-BIR3 segment of cIAP1. After a 30-min incubation of S100 with cytochrome c and ATP as described under “Experimental Procedures,” the apoptosome reaction was stopped by dilution with caspase assay buffer. Caspase-3 activity was determined with Ac-DEVD-AMC as substrate. C, effect of IAPs on already activated caspase-3-like activity. The caspase-3 activity of the S100 fraction was activated by the addition of cytochrome c and ATP in the absence of an added IAP. Caspase activation was stopped by diluting a sample of the apoptosome reaction by 10-fold into caspase assay buffer that contained the indicated micromolar concentration of each GST-IAP. Values are means ± S.E. (n = 3). Control activity was 12.2 ± 1.3 nmol of AMC produced per mg/min. *, statistically significant effect of XIAP (p < 0.01) by analysis of variance (GraphPad Prism 5).