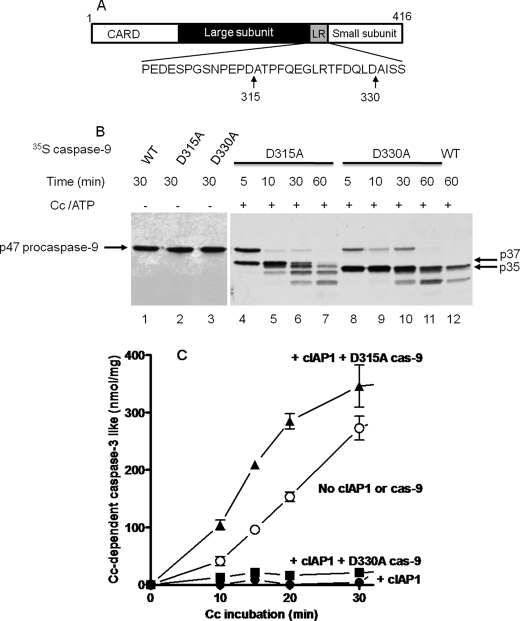
FIGURE 3.
The procaspase-9 D315A mutant, but not the D330A mutant, reverses the inhibition of the cytochrome c-dependent apoptosome by cIAP1. A, schematic of human procaspase-9 and the positions of the autocatalytic cleavage site (Asp-315) and the caspase-3 cleavage site (Asp-330) within the linker region (LR) between the large and small subunits of mature caspase-9. B, autoradiogram showing the processing of 35S-labeled p47 procaspase-9 mutants (D315A and D330A) by the apoptosome. The experiment was done as described in the Fig. 2B legend except the 35S-labeled procaspase-9 used was wild-type or the indicated point mutant. C, the procaspase-9 D315A mutant, but not the D330A mutant, prevents cIAP1 inhibition of the apoptosome. The cytochrome c (Cc)-dependent apoptosome activation of procaspase-3 was assayed as described for B in the presence (▲, ■, and ●) or (○) absence of 500 nm GST-cIAP1. The indicated D315A or D330A mutant of procaspase-9 (cas-9; 4 μl of TnT reaction/20 μl of apoptosome reaction) was added to the apoptosome reaction. Samples (4 μl) of the apoptosome reaction were removed after the indicated intervals, diluted 10 times with caspase assay buffer, and assayed for caspase-3-like activity with Ac-DEVD-AMC as substrate. Values are means ± S.E. (n = 3) for AMC produced (nmol/mg of S64 protein).