FIGURE 7.
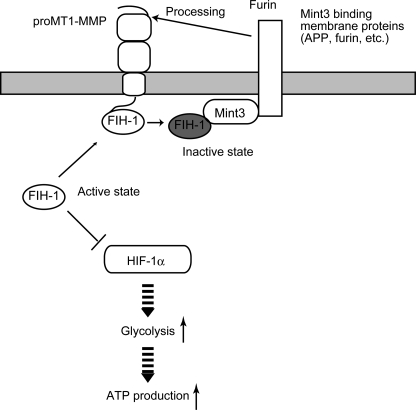
The MT1-MMP CPT enhances the transcriptional activity of HIF-1 via suppression of FIH-1. MT1-MMP and Mint3 localize to the plasma membrane compartment, particularly within the Golgi. FIH-1 localizes predominantly to the cytoplasm, where it inhibits the transcriptional activity of HIF-1α. The CPT of MT1-MMP is able to bind FIH-1. Although this association is not stable, it recruits the cytoplasmic FIH-1 to the Golgi. Mint3 lines the plasma membrane within the Golgi by binding to membrane proteins, such as furin and APP, via its C-terminal domain, which is separated from its FIH-1 binding domain located at the N terminus (supplemental Fig. S4). Furin is a protease that binds MT1-MMP, cleaves the propeptide sequence of MT1-MMP, and converts pro-MT1-MMP into the mature enzyme. Thus, if FIH-1 binds transiently to the CPT of MT1-MMP, it may increase the odds of FIH-1 encountering Mint3 localized in the vicinity of MT1-MMP. Indeed, the overexpression of MT1-MMP CPT induces the suppression of FIH-1 activity by Mint3. The suppression of FIH-1 enhances HIF-1 activity and augments ATP generation by glycolysis in macrophages.