FIGURE 1.
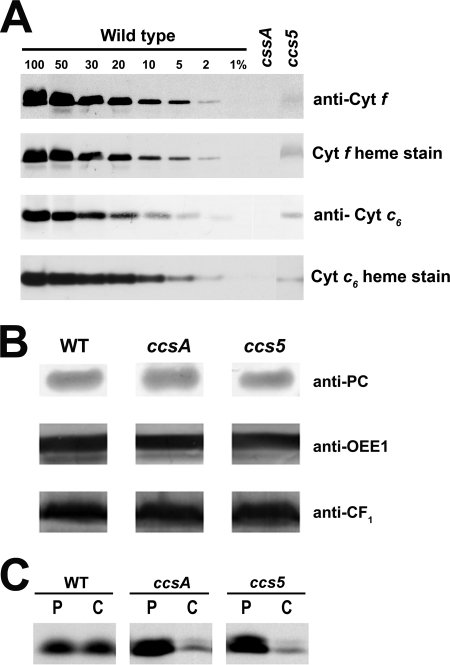
T78 displays a dual deficiency in holocytochrome f and c6. A and B, accumulation of plastid c-type cytochromes in the T78 mutant. Soluble and membrane fractions of copper-deficient cultures were analyzed for the accumulation of cytochrome f (anti-cyt f and cyt f heme stain) and cytochrome c6 (anti-cyt c6 and cyt c6 heme stain), respectively. All the samples were found to be copper-deficient based on the absence or very low abundance of immunoreactive holoplastocyanin (data not shown). Samples of wild type strains (WT), T78 mutant (ccs5), and B6 (ccsA) corresponding to 5 μg of chlorophyll were separated in SDS-containing acrylamide (12%) gels or native acrylamide gels (15%) to detect cytochrome f and cytochrome c6, respectively. For an estimation of the cytochrome abundance, dilutions of the wild type sample (arg7cw15A for cytochrome f and CC125 for cytochrome c6) were loaded on the gel. Gels were then transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes following electrophoresis before heme staining by chemiluminescence and immunodecoration with antisera against Chlamydomonas cytochrome f and cytochrome c6 in A and with antisera against plastocyanin, OEE1, ATPase CF1 in B. C, in vivo synthesis and degradation of apocytochrome f in the ccs5 mutant. The synthesis of cytochrome f was assessed by immunoprecipitation of anti-cytochrome f-reactive polypeptides from solubilized acetone extracts of wild type (WT), B6 (ccsA), and T78 (ccs5) cells labeled for 10 min with Na235SO4 (P indicates pulse). The labeled cells were sampled 40 min later after further incubation in the presence of unlabeled sulfate and chloramphenicol to assess the fate of the newly synthesized protein (C indicates chase). Immunoprecipitates were resolved by denaturing gel electrophoresis followed by fluorography.