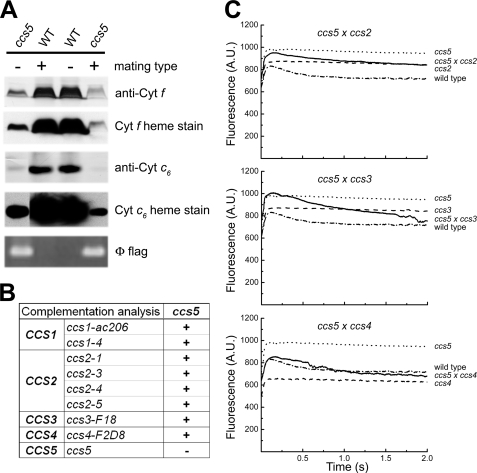
FIGURE 2.
T78 mutant defines a new CCS locus (CCS5). A, monogenic Mendelian segregation of the ccs mutation in T78. Two spores displaying the photosynthetic deficient phenotype (ccs5) (left, T78.5a− and right, T78.5d+) and two wild type spores (WT) from the same tetrad were used to analyze accumulation of plastid cytochromes (cyt) c by heme stain and immunoblotting. The tetrad originates from a cross of the T78 insertional mutant to a wild type strain (CC621). The mating type mt+ or mt− of each spore is indicated. Segregation of the Φ flag in the progeny was followed by PCR amplification from total genomic DNA samples of the molecular tag using diagnostic primers. B, complementation of ccs5 mutant with strains carrying alleles of the CCS1, CCS2, CCS3, and CCS4 loci. Diploid zygotes were obtained by crossing ccs5 mutant strains by strains carrying the ccs1-ac206, ccs1-4, ccs2-1, ccs2-3, ccs2-4, ccs2-5, ccs3-F18, and ccs4-F2D8. “+” indicate a positive complementation based on the presence of the decay phase in fluorescence induction experiments. “−” indicates a negative complementation. C, fluorescence kinetics indicate restoration of cytochrome b6f in the diploid zygotes. Fluorescence induction and decay kinetics of the ccs5xccs2-5, ccs5xccs3-F18, and ccs5xccs4-F2D8 diploid zygotes, respective parental strains (see B), and wild type strain (arg7cw15A). The fluorescence transients were measured using a homemade device. The fluorescence is in arbitrary units (A.U.) and recorded over a 2-s illumination period. The rise and plateau curve for the ccs mutants is the signature of a specific block in electron transfer at the level of cytochrome b6f complex because of its impaired assembly in the absence of membrane-bound holocytochrome f. When the energy absorbed by the chlorophyll cannot be utilized because of a block in photosynthetic electron transfer through cytochrome b6f, an increase in the chlorophyll fluorescence is observed. Note the absence of the decay phase corresponding to reoxidation of the quinone pool (the primary electron acceptor of photosystem II) by the cytochrome b6f complex. In the complemented diploid zygote, the presence of the decay phase indicates restoration of the b6f complex function.