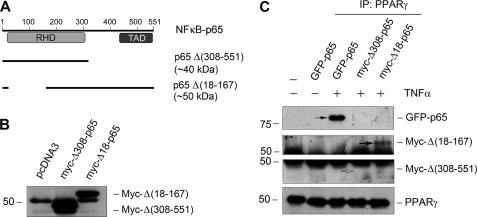
FIGURE 7.
C-terminal p65 NF-κB mediates its interaction with PPARγ. A, diagram shows the construction of various p65 NF-κB expression vectors. Plasmids containing GFP-tagged full-length p65 as well as Myc-tagged p65 deletion mutants are illustrated. The calculated molecular masses of these mutant proteins are shown. RHD, Rel homology domain; TAD, trans-activation domain. B, mesangial cells were transfected with Δ(308–551) and Δ(18–167) truncated vectors and pcDNA3 control, followed by Western blotting for Myc. Myc-tagged Δ(308–551) (44 kDa) and Δ(18–167) (56 kDa) are indicated. The discrepancy between the predicted and actual molecular masses of the mutant proteins presumably resulted from the posttranslational modifications. C, mesangial cells were transfected to express GFP-tagged full-length p65 as well as Myc-tagged truncated p65 mutants Δ(308–551) and Δ(18–167). After treatment with TNF-α (5 ng/ml), cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-PPARγ, followed by immunoblotting with anti-GFP and anti-Myc, respectively. Interaction of PPARγ with full-length p65 and Δ(18–167) (solid arrows), but not Δ(308–551) (open arrow), was evident.