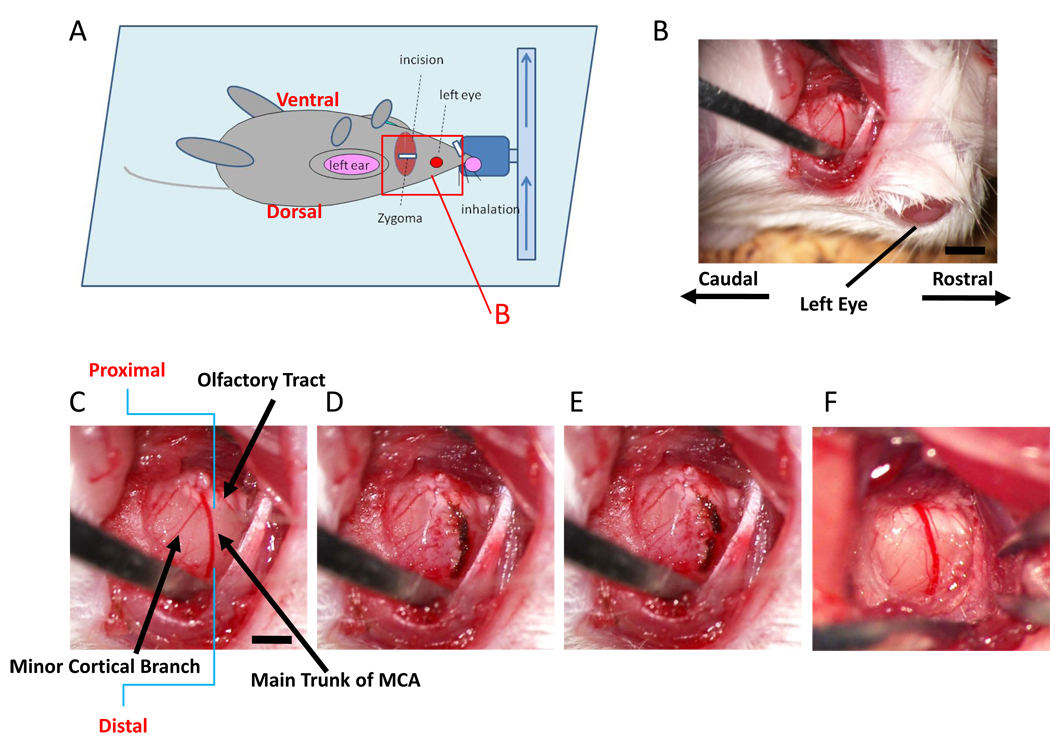
Figure 1. Ligation of the distal portion of MCA.
(A) Schematic depiction showing orientation of the animal in our model for induction of stroke. The red rectangle represents the portion shown in panel B. (B–E) After dissecting the left zygoma, a hole was made and the dura was carefully removed (B; lower magnification, C; higher magnification). The main trunk of the MCA was electrocoagulated (D) and disconnected using the tip of 30G needle (E). This mouse had a minor cortical branch (C), but electrocoagulation and disconnection of main trunk resulted in disappearance of blood flow in the minor cortical branch. Panel (F) shows a representative picture of the vascular structure without a minor cortical branch around olfactory tract. Scale bar: 1 mm (B) and 0.5 mm (C).