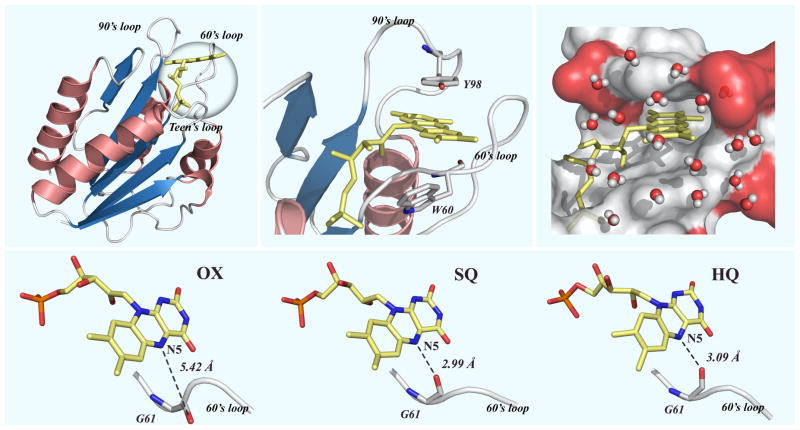
Figure 1.
Top panel: (Left) The x-ray crystal structure of oxidized D. vulgaris flavodoxin (PDB: 3FX2). (Middle) Close view of the FMN binding site embraced by two 60’s and 90’s loops. The FMN cofactor is sandwiched by two aromatic resides of W60 and Y98. (Right) Surface-map representation of a snapshot of 1-ns MD simulations, showing the function site with hydrating water molecules within 6 Å from the isoalloxazine ring and neighboring negatively-charged residues (red). Lower panel: The local x-ray structures of three redox states show the loop flipping in SQ and HQ states to form a hydrogen bond with N5 of the isoalloxazine ring.