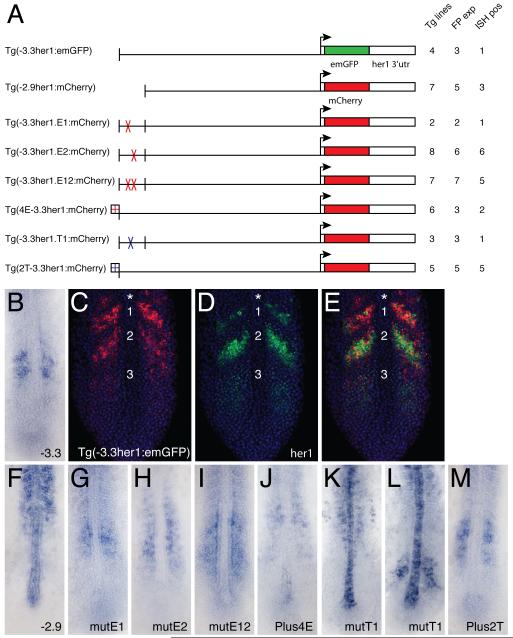
Fig.4. Transgenic analysis of the function of protein binding sites in the ASE.
(A) Schematic representation of the transgenic constructs used to analyze the function of protein binding sites within the ASE. For each construct: Tg lines = the total number of transgenic lines identified, including those only detected by PCR; FP exp = the number of transgenic lines in which expression was observable by fluorescence; ISH pos = the number of transgenic lines that exhibited expression that was detectable by in situ hybridization. (B) Standard in situ hybridization for emGFP mRNA in a transgenic embryo carrying the (−3.3her1:emGFP) construct. (C-E) Double fluorescent in situ hybridization of a Tg(−3.3her1:emGFP) embryo, showing either emGFP (C, red) or her1 (D, green) expression, or both (E). Nuclei stained with propidium iodide are colored blue. The same confocal section is shown in all panels. Numbers indicate specific stripes of gene expression as referenced in the text. Asterisk indicates the additional more anterior stripe seen in transgenic embryos. (F-M) Standard in situ hybridizations showing reporter gene (emGFP or mCherry) expression in transgenic embryos carrying the indicated constructs.