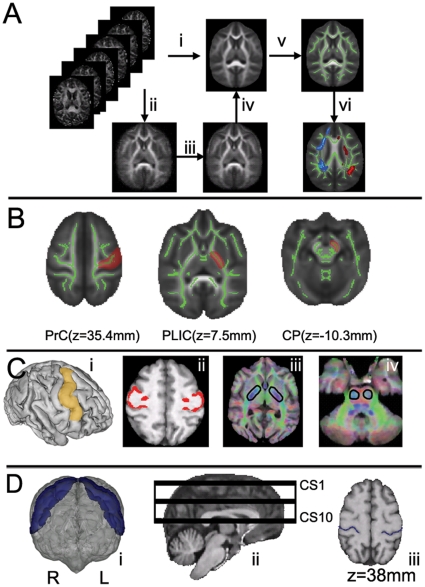
Figure 1. Procedures for TBSS, masks in tractography, and measurement of CS depth.
A: Image registration procedure for TBSS: All subjects' FA images were registered on a cohort-specific template (A.i.). A three-stage procedure was used for generating the cohort-specific FA template. First, a randomly selected subject's FA map was aligned so that the midsagittal plane was defined by the interhemispheric fissure of the brain, the axial plane was situated parallel to the bicommissural line (anterior commissure and posterior commissure), and the origin of the space was defined as the center of the anterior commissure. Then, all of the other FA maps were aligned to the first FA map using rigid body registration with six degrees of freedom (A.ii.). The individually aligned FA maps were then averaged to generate a template with six degrees of freedom. Second, the FA template (6 degrees of freedom) was employed as the initial FA template on which each subject's FA map was registered using twelve degrees of freedom affine registration (A.iii.). These were then averaged to create an intermediate FA template (12 degrees of freedom) for the final alignment of the FA maps using nonlinear registration (A.iv.). This population-specific FA template obtained with nonlinear registration was then used as the template for TBSS registration. Then, a symmetrical FA skeleton for each FA image was derived representing the centers of all tracts common to all the chimpanzees (A.v.). FA and FA difference maps derived from the symmetrical FA skeleton were then evaluated with permutation-based statistics to test for left-right differences (A.vi.). B: The locations of the three ROIs in the skeleton-based ROI analysis. C: The cortical mask, waypoint mask and seed mask used in tractography for deriving the precentral corticospinal tract. The schematic in C.i. shows the coverage of the precentral GM/WM boundary cortical masks. C.ii. provides a 2D view of the precentral GM/WM boundary cortical masks at an axial slice, while C.iii. shows the waypoint mask at the posterior limb of internal capsule, and C.iv. shows the seed mask at the level of the pons. D: The schematic of the depth of the CS. The schematic of the CS in a 3D view (D.i.); the intrasulcal length of the posterior contour of the precentral gyrus was traced in a dorso-ventral sequence of 45 slices extending from z = 9∼45 mm covering the primary motor cortex, which was subsequently divided into ten evenly spaced subsections from the most ventral region (CS1) to the most dorsal region (CS10) (D.ii.). The horizontal black bands illustrates the relatively volume covered in each subregion. An example slice at z = 38 mm was shown in D.iii., with the traced depth of the CS denoted as blue color.