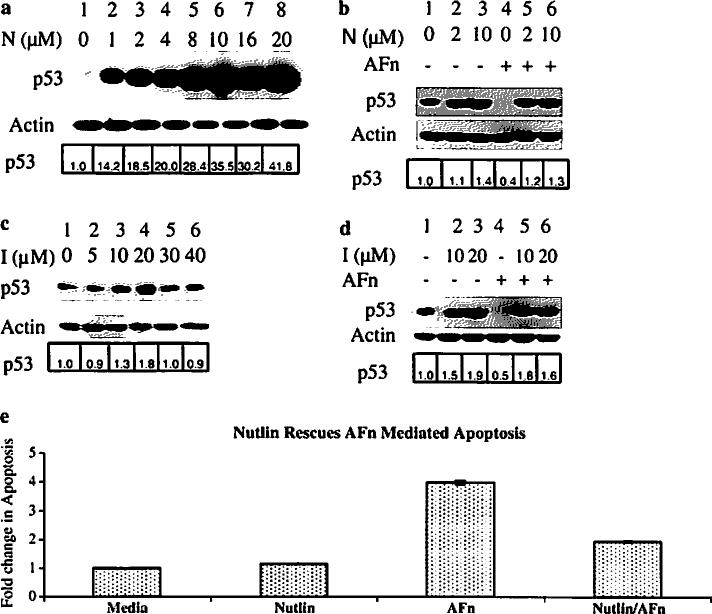
Fig. 1.
Inhibiting the binding of Mdm2 to p53 prevents p53 degradation under anoikis conditions. Human primary ligament fibroblasts were treated with various concentrations of Nutlin (N) or (c), a different Mdm2 inhibitor (I) for 7 h and lysed, and the p53 level was determined by Western blotting with an anti-p53 antibody. b Based on the results from the dose–response experiments in (a) and (c), cells were pretreated with chosen concentrations of Nutlin or (d), Mdm2 inhibitor or control medium for 2 h and then treated with the fibronectin fragments in presence of the drugs for 7 h. Cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to p53 and Mdm2. Actin served as a loading control. e Human primary ligament fibroblasts were treated with 10 μM Nutlin for 2 h and then treated with the fibronectin fragments or control medium in presence of the drugs for 7 h. Cell lysates were prepared and analyzed for apoptosis using the Cell Death Detection ELISAPLUS (Roche). The relative fold change in p53 expression was analyzed by densitometry and expressed with respect to p53 in lane 1 for all the figures