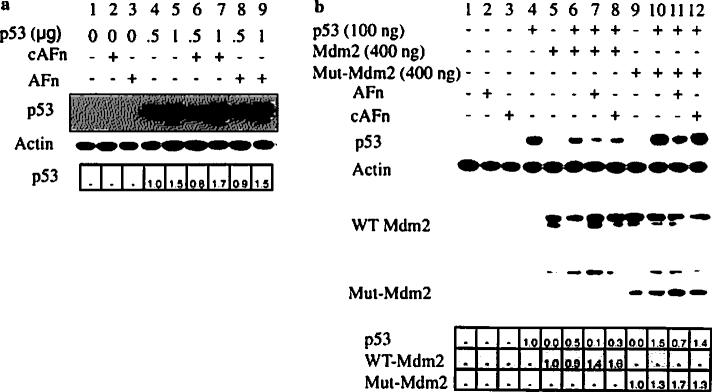
Fig. 4.
Mdm2 null and mutant conditions resist p53 degradation triggered by anoikis. a p53/Mdm2-null cells were transfected with wildtype p53, treated with recombinant fibronectin fragments, lysed, and analyzed for p53 expression by Western blotting. b p53/Mdm2-null cells were transfected with wildtype p53 or cotransfected with wildtype p53 and wildtype Mdm2 (WT Mdm2) or wildtype p53 and mutant Mdm2 (Mut-Mdm2). Thirty-six hours after transfection, the cells were treated with recombinant fibronectin fragments or control medium, and lysed. p53 and Mdm2 protein expressions were determined by Western blot. Cells upon transfection with wild type Mdm2 or mutant Mdm2 cDNA showed decreased levels of Mdm2 protein expression. The relative fold change in p53 or Mdm2 expression was analyzed by densitometry and expressed with respect to p53 in lane 4 in Fig. 4a and b and lane 5 for wild type Mdm2 and lane 9 for mutant Mdm2 in Fig. 4b