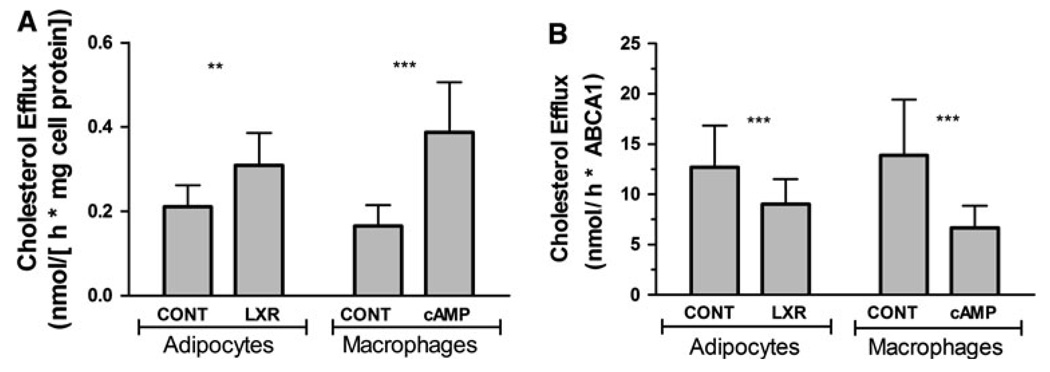
Fig. 3.
Effect of ABCA1 expression levels in apoA-I-dependent CL Efflux from adipocytes or macrophages. a Rates of CL efflux normalized by total cellular protein content. The experiments were performed as indicated in “Materials and methods” section. The cells were mock-treated (CONT) or treated with either the LXR-agonist, 2 µM GW3965 (LXR), or 180 µM 8-Br-cAMP (cAMP) for 24 h prior to assays. The rates of apoA-I-induced CL efflux normalized by protein content were determined from the slopes of the time courses (% of cellular CL released into medium vs time). The mean values ± SD for adipocytes were obtained from three independent experiments and include 19 data points. The data for macrophages were obtained from four experiments (n = 15). The differences between the means of control and treated cells were significant (P < 0.001) for both adipocytes and macrophages. b Rates of CL efflux normalized by ABCA1 protein levels. The average rates of apoA-I-induced CL efflux shown in Fig. 3a were converted into nmoles of CL/h-ABCA1 protein using the average relative levels of ABCA1 expression shown in the Fig. 2b and the cholesterol contents of the cells. The lipid compositions of control and treated homogenates showed no significant differences. Each bar represents the mean ± SD. The SDs were calculated using the propagation of errors equation and the SD of ABCA1 levels and rates of efflux. The differences between the means of control and treated cells were significant (P < 0.001) for both adipocytes and macrophages