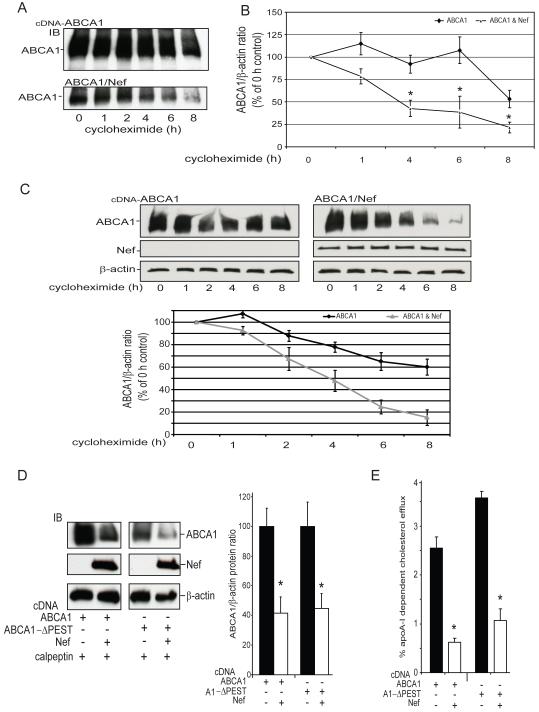
Figure 4. Nef down-regulates ABCA1 protein expression by a mechanism that stimulates degradation of the transporter but does not depend upon the ABCA1 PEST motif.
To determine the effect of Nef expression on the degradation of ABCA1, 293ET cells expressing ABCA1 alone or in the presence of Nef were treated with the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide for the indicated time periods. A, Immunoblots are shown of ABCA1 expression in the presence and absence of Nef. B, The ABCA1β-actin protein ratio was quantitated using BioRad ECL imaging and expressed as a percentage of the ABCA1 level in cells treated with vehicle only (0 h) [n=3 (1 and 6 h), n=5 (0, 4, 8 h), ±SEM, *p<0.05, ABCA1 versus ABCA1 & Nef]. C, Nef expression in RAW264.7 macrophages also significantly accelerates the degradation of endogenously expressed ABCA1 induced by treatment with an LXR agonist (TO-901217, 1uM, 24h). Representative immunoblots of ABCA1, Nef and β-actin are shown in the top panels and the ABCA1/β-actin protein is graphed below (n=2, ±SEM, p<0.01, ANOVA) D, Nef is able to significantly suppress the expression of ABCA1 and the ABCA1ΔPEST mutant and this effect is not block by calpain protease inhibitor calpeptin (N=3, ±SD, *p<0.05, ABCA1 versus ABCA1 & Nef). E, Nef is able to significantly suppress the cholesterol efflux activity of ABCA1 and the ABCA1ΔPEST mutant (N=3, ±SD, *p<0.05, ABCA1 versus ABCA1 & Nef). Results in A-E are representative of two or more experiments.