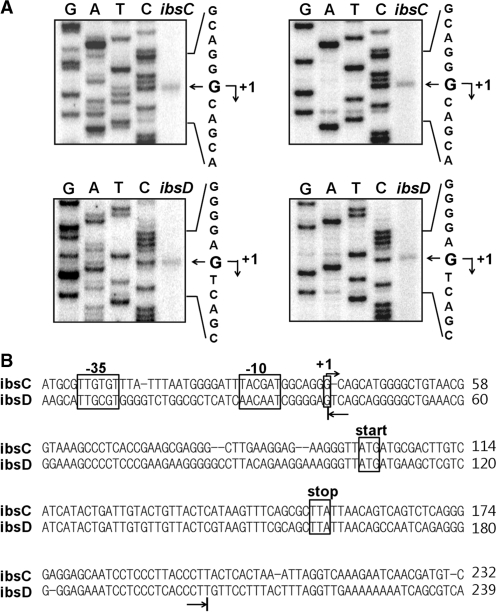
Figure 4.
Identification of the ibsC and ibsD transcriptional start sites. Total cellular RNAs were prepared from cells containing the ibsC-CAT or ibsD-CAT fusion plasmid, then subjected to primer extension analysis. (A) Extension products from two different primers cat1 (left) and cat2 (right) were electrophoresed on a 5% polyacrylamide sequencing gel containing 7 M urea. The DNA sequencing ladders were prepared using the same primers and ibsC-CAT or ibsD-CAT fusion plasmid DNA as the template. (B) Promoter elements are shown in the ibsC or ibsD sequence. Transcription start sites determined by primer extensions analysis are indicated by arrows. The 5′ and 3′ ends of in vitro-transcribed ibsC and ibsD RNA used for the in vitro binding assay and structural mapping in this study are indicated by the arrows below the sequences.