FIG. 3.
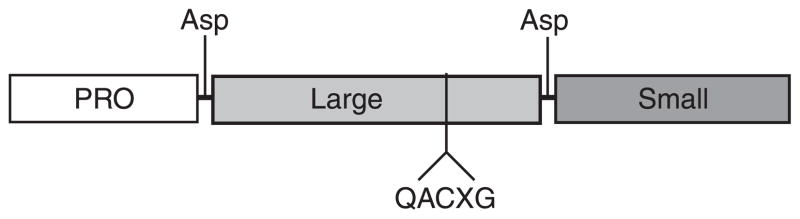
Caspase structure. Caspases consist of a catalytic domain organized in a large subunit (~20 kDa), a small subunit (~10 kDa), and a prodomain of variable length. Effector caspases exhibit a short prodomain, whereas initiator caspases have long prodomains that direct binding to protein complexes. Caspase-directed cleavages at aspartate residues in a linker region between the large and the small subunit and between the prodomain and the large subunit generate the formation of the 20- and 10-kDa polypeptides that oligomerize to form the heterotetrameric active form of protease. The catalytic cysteine is embedded in the conserved pentapeptide QACXG motif within the large subunit.