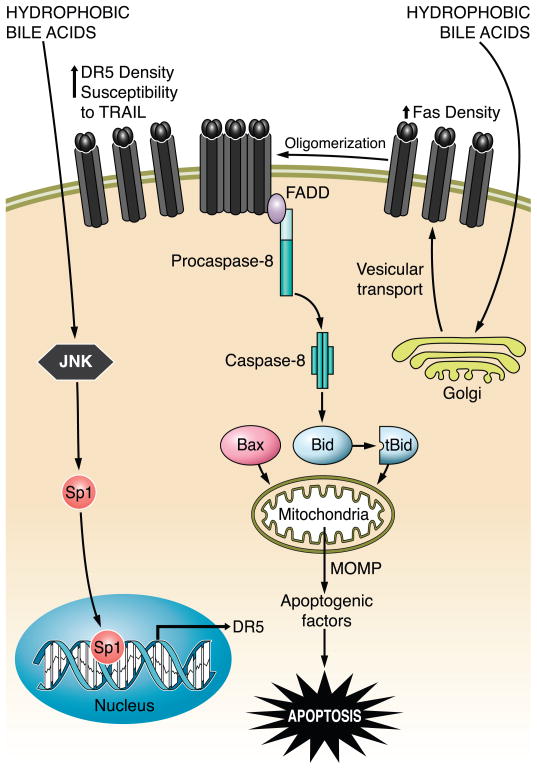
FIG. 8.
The bile acid-induced/death receptor-mediated apoptosis pathway. Hydrophobic bile acid stimulates Golgi-associated and microtubule-dependent Fas trafficking to plasma membrane, resulting in an increased density of cell surface Fas. In a FasL-independent manner, Fas undergoes oligomerization and recruits FADD, which, in turn, binds to pro-caspase 8 and facilitates its activation by autocatalytic processes. Active caspase 8 cleaves Bid, whose truncated form translocates to mitochondria and cooperates with Bax to induce MOMP. This results in release of apoptogenic factors, such as cytochrome c, AIF, and SMAC, into the cytosol, which ultimately promote the activation of effector caspases 3, 6, and 7 and cell death. At the same time, hydrophobic bile acids also cause upregulation of death receptor 5 (DR5) via JNK-mediated activation of the transcription factor Sp1 (specificity protein 1), sensitizing the hepatocytes to TRAIL-induced apoptosis.