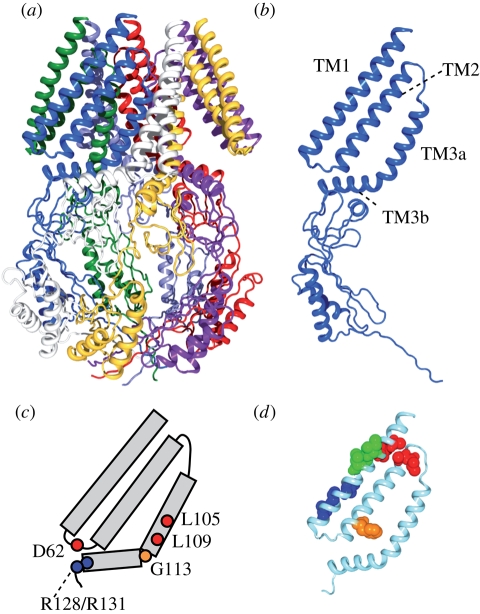
Figure 4.
Structure and function of the MscS mechanosensitive channel. (a) Crystal structure of E. coli MscS (PDB accession number: 2OAU). Each subunit is in a different colour. (b) Structure of single subunit of MscS. Indicated are the first and second transmembrane helices (TM1 and TM2) and the third transmembrane helix, which is separated into two by a kink at G113 (TM3a and TM3b). (c) Important residues for the function of MscS. L105 and L109 form the constriction of the pore. D62 forms a salt bridge with R128 and R131. A kink at G113 occurs in the inactive state. (d) The gating threshold increases on asparagine substitution at the residues indicated by red (A34, I37, A85, L86), blue (I48, A51, L55), and orange (F68). Conversely, the threshold decreases on mutation at I39, V40 and I43 (green). Data from Nomura et al. (2006) and Okada et al. (2002).