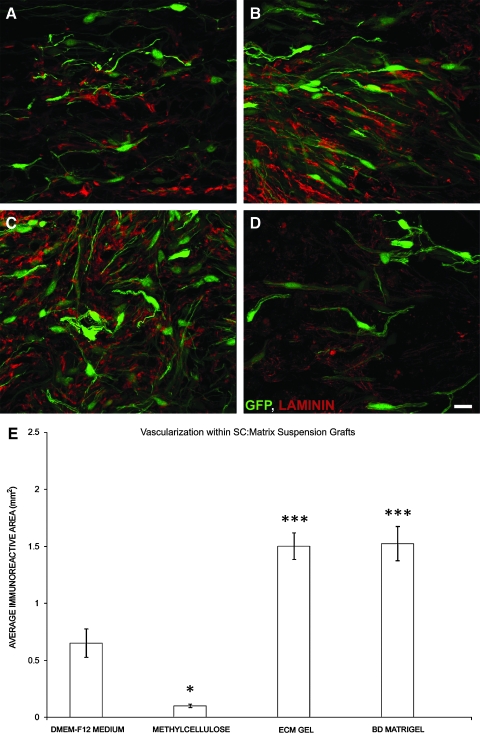
FIG. 3.
BD Matrigel and ECM gel, but not methylcellulose, improve SC implant vascularization over cell:medium suspensions (A–D). To determine the degree of GFP-SC implant vascularization, immunostaining for laminin (red) was performed, and the area of immunoreactivity within the implant quantified. Compared to medium (A), suspension of GFP-SCs in either ECM gel (B) or BD Matrigel (C), but not methylcellulose (D), significantly increased the amount of filamentous laminin within the implant. Scale bar: 20 μm. (E) Quantification of the area of filamentous laminin within the implants revealed greater vascularization with ECM gel and BD Matrigel over medium controls; significantly less vascularization was observed with methylcellulose suspension. Statistical significance indicated at *p < 0.05 or ***p < 0.001. Color image is available online at www.liebertonline.com/neu.